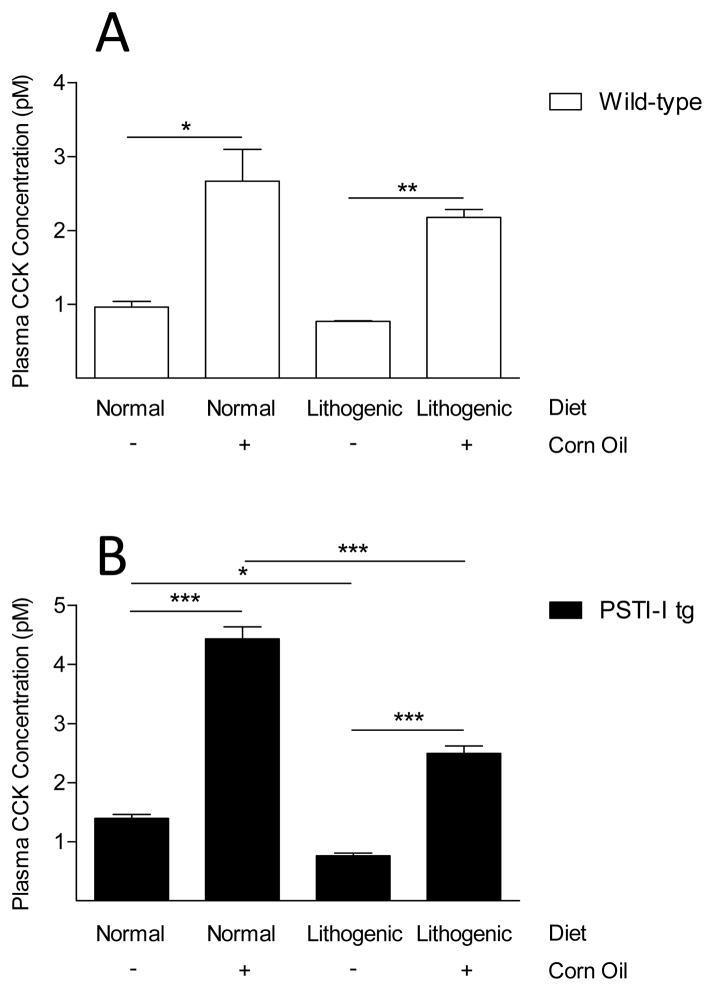
Figure 6.
Comparison of fasted and fed plasma CCK concentrations in wild-type mice (A; open bars) and PSTI-I tg mice (B; filled bars) eating a normal or a lithogenic diet. The fasted and fed results for the mice eating the normal diet are reproduced from Figure 1 for comparison to the results for the mice eating the lithogenic diet. Eating a lithogenic diet reduced both fasting and fed plasma CCK concentrations in wild-type mice (A) and in PSTI-I tg mice (B). However, the reductions of CCK levels were not only greater in the PSTI-I tg mice than in the wild-type mice but were also statistically significant in the PSTI-I tg mice but not in the wild-type mice. (* P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001)