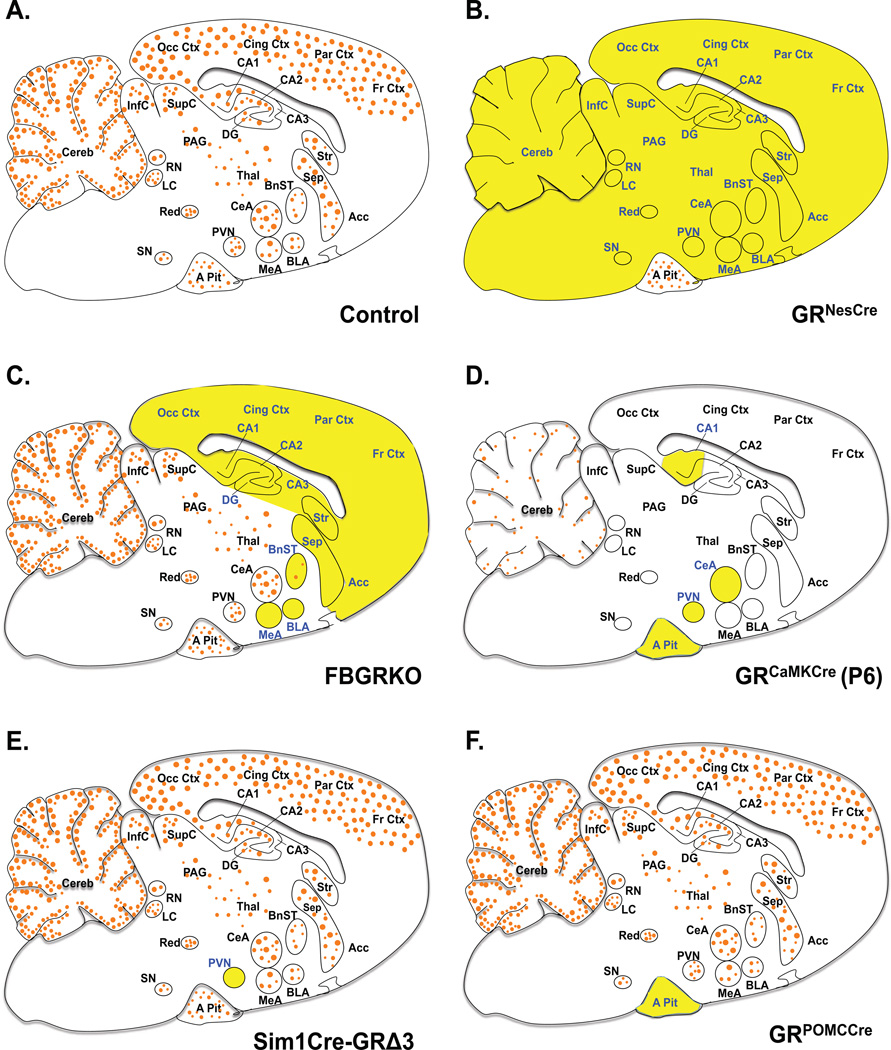
Figure 1. Glucocorticoid Receptor Expression in Genetic Mouse Models.
Sagittal brain sections depicting areas of GR mRNA expression and deletion in mice with targeted GR deletion. Orange circles (●) represent GR and targeted regions are in yellow highlight and blue font. A. Adult control mice ubiquitously express GR mRNA in the entire brain and pituitary, with higher expression in limbic regions. B. Adult GRNesCre mice have GR loss in the entire brain, neurons and glial cells. C. FBGRKO mice have GR loss in forebrain neurons during adulthood. D. At postnatal day 6 GR expression is low and limited to few brain region (blue font). GRCaMKCre mice have GR loss in most of the neurons in brain and cells in the pituitary at P6. E. Adult Sim1Cre-GRe3Δ mice have GR loss primarily in PVN neurons. F. GRPOMCCre mice have GR loss in the anterior pituitary cells throughout life. Abbreviations: Anterior pituitary, A Pit; Basolateral nucleus of the amygdala, BLA; Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, BnST; Central nucleus of the amygdala, CeA; Hippocampal areas, CA1, CA2, CA3; Cerebellum, Cereb; Cingulate cortex, Cing Ctx; Dentate gyrus, DG; Frontal cortex, Fr Ctx; Inferior colliculus, InfC; Locus coeruleus, LC; Medial nucleus of the amygdala, MeA; Occipital cortex, Occ Ctx; Periaqueductal gray, PAG; Parietal cortex, Par Ctx; Paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, PVN; Raphe nucleus, RN; Septum, Sep; Supraoptic nucleus, SN; Superior colliculus, SupC; Thalamus, Thal;