Figure 2.
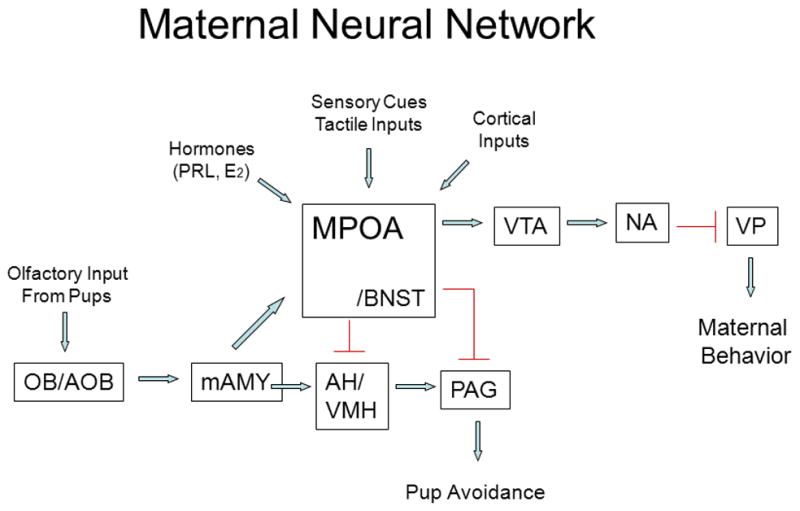
Schematic representation of key neural regions and connections that constitute the maternal neural network. Arrows are stimulatory except that from the AH/VMH to the PAG which is inhibitory. AH, anterior hypothalamus; AOB, accessory olfactory bulb; BNST, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; mAMY, medial amygdala; MPOA medial preoptic area; NA, nucleus accumbens; OB, olfactory bulb; PAG, periaqueductal gray; VMH, ventromedial hypothalamus; VP, ventral pallidum; VTA, ventral tegmental area. Taken from Bridges, R.S., Nephew, B.N., 2009. Neuroendocrine control: maternal behavior. In Encyclopedia of Neuroscience, volume 6, pp. 333–342, with permission, Elsevier Ltd.
