Figure 7.
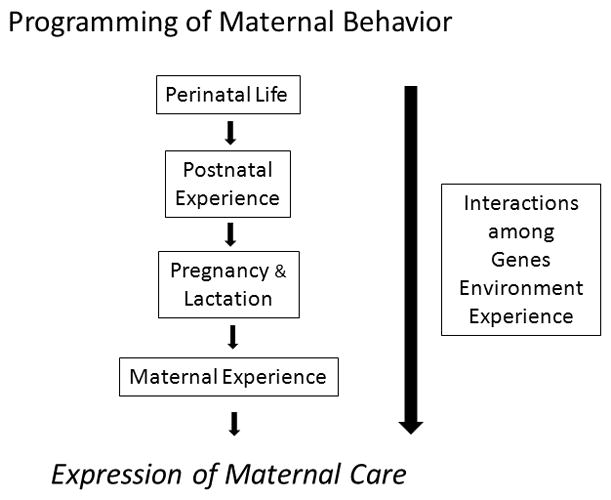
The developmental programming of maternal behavior begins during prenatal life, continues postnatally, and throughout adult development. Genetic factors together with epigenetic and experiential behavioral inputs modify the expression of maternal care over the female’s lifespan. The types and extent of maternal experience can enhance or interfere with maternal care with repeated parenting bouts generally strengthen maternal proficiency.
