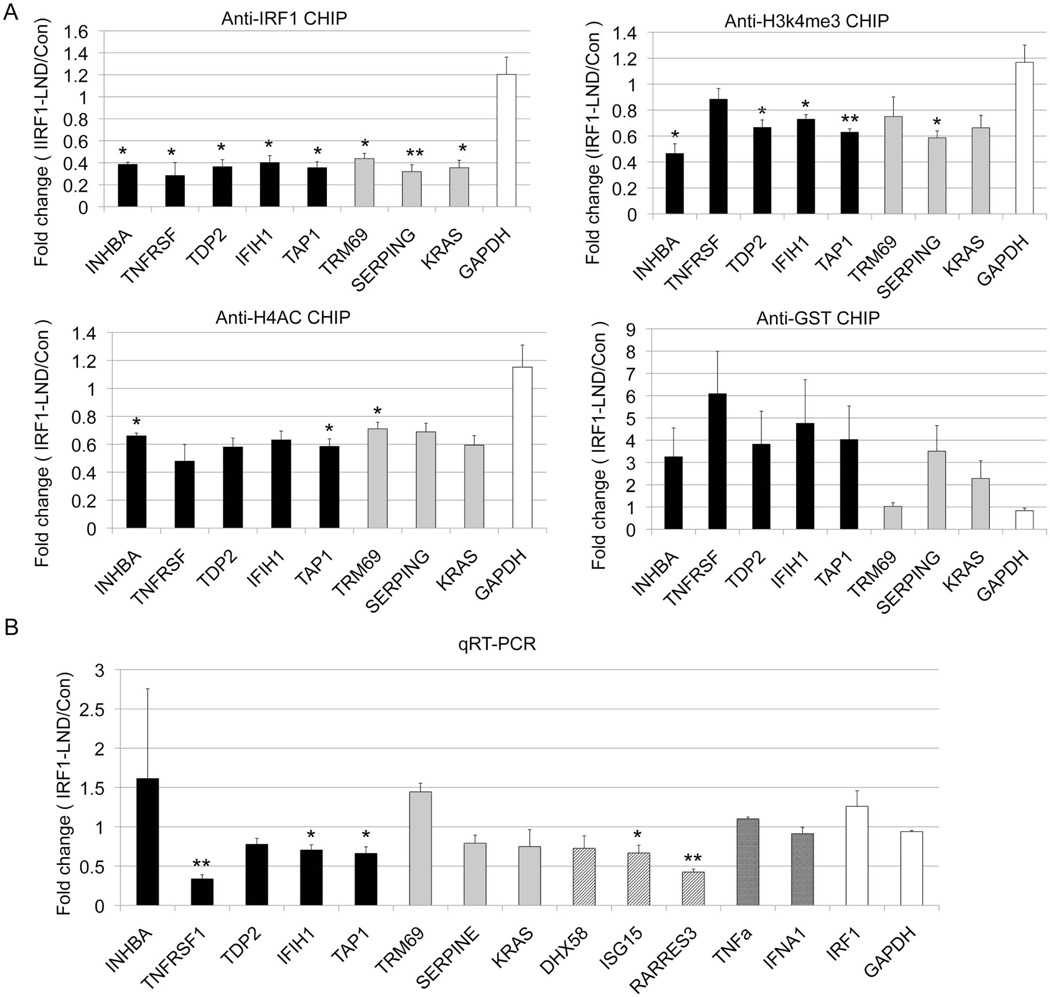
Figure 5.
The effect of IRF1 decoy treatment. D54MG cells were transfected with the IRF1 decoy oligonucleotide (IRF1-LND) or the control oligonucleotide (Con). A) The cells were immunoprecipitated with the indicated antibody, GST is a control non-binding antibody. The effect of the IRF1 decoy was defined by qPCR. B) RNA was harvested and cDNA was quantitated using qRT-PCR. .INHBA, TNFRSF14, TAP1, TDP2 represent the target genes with both increased IRF1 binding and mRNA expression in SLE patients (black bar). TRIM69, SERPINE1 and KRAS represent potential IRF1 targets(grey bar). The diagonal lines signify genes with very high IRF1 peaks (DHX58, ISG15, RARRES3, IFIH1). The cross hatched bars signify genes with potential IRF1 binding sites (TRIM69, SERPINE1, KRAS). IRF1 and GAPDH are shown as controls. GAPDH is unaltered in SLE. Error bars indicate standard error. N=3. Student's t-test was used to determine statistical significance (* indicates p<0.05, ** indicates p<0.005).