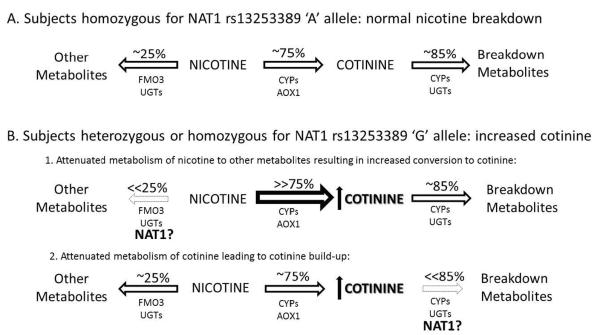
Figure 4.
Potential mechanisms by which NAT1 modulates cotinine levels. (A) In subjects homozygous for the major NAT1 `A' allele, 75% of nicotine is broken down to cotinine and 25% to other metabolites. (B) The minor NAT1 `G' allele might affect cotinine levels by (1) regulating acetylation of an unknown nicotine metabolite or intermediate decreasing the breakdown of nicotine, resulting in a compensatory increase in cotinine formation; or (2) There might be an unknown intermediate that requires acetylation by NAT1 to further metabolize cotinine, and mutations in NAT1 could block this pathway, resulting in an accumulation of cotinine.