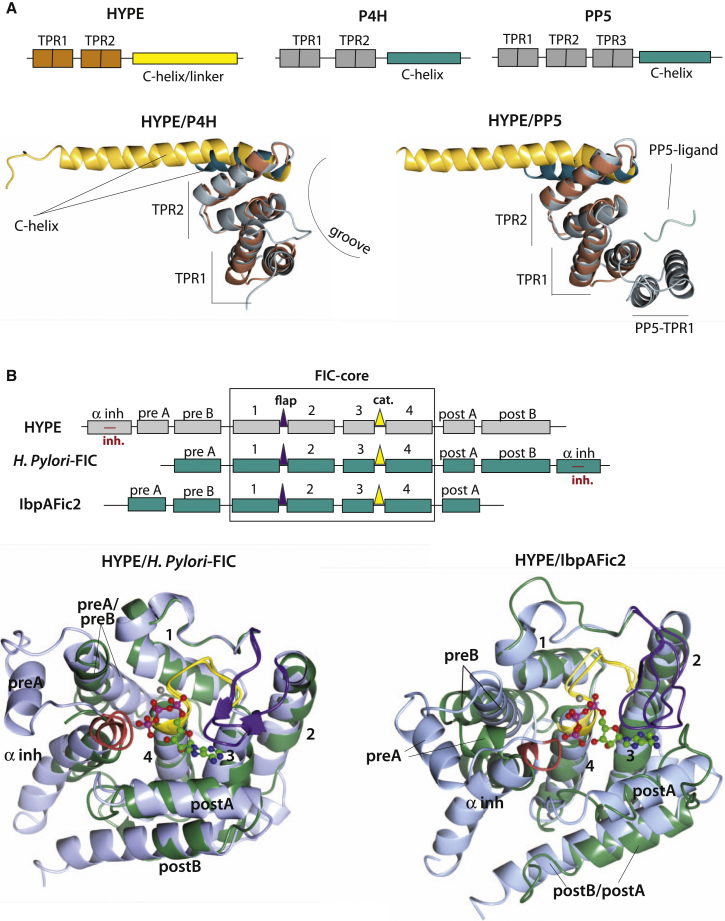
Figure 2.
Features of TPR and FIC Domains
(A) Schematic diagrams (top) and structural comparison (bottom) of TPR domain from HYPE with P4H TPR domain (left, 1TJC) and PP5 TPR domain (right, 2BUG). Position of a peptide from Hsp 90, binding to the TPR groove in PP5 is also shown (right).
(B) Schematic diagrams (top) and structural comparison (bottom) of FIC domain from HYPE with H. Pylori FIC (left, 2F6S) and IbpA2Fic (right, 4ITR). Positions of the catalytic loop (yellow), flap (purple), and inhibitory motif (red) are shown, as well as the position of ATP-cofactor from structure of E234G HYPE. FIC-domain core (FIC-core) α helices are labeled as 1–4. The last, αinh helix from H. Pylori FIC is circularly permuted and overlays with the αinh helix from HYPE FIC. IbpAFic2 lacks an αinh helix. Pre B α helix from HYPE FIC overlays with pre A α helix from H. Pylori FIC, while post B α helix from HYPE FIC overlays with post A α helix from IbpAFic2. See also Figure S5.