Figure 7.
AMPylation Activity of HYPE
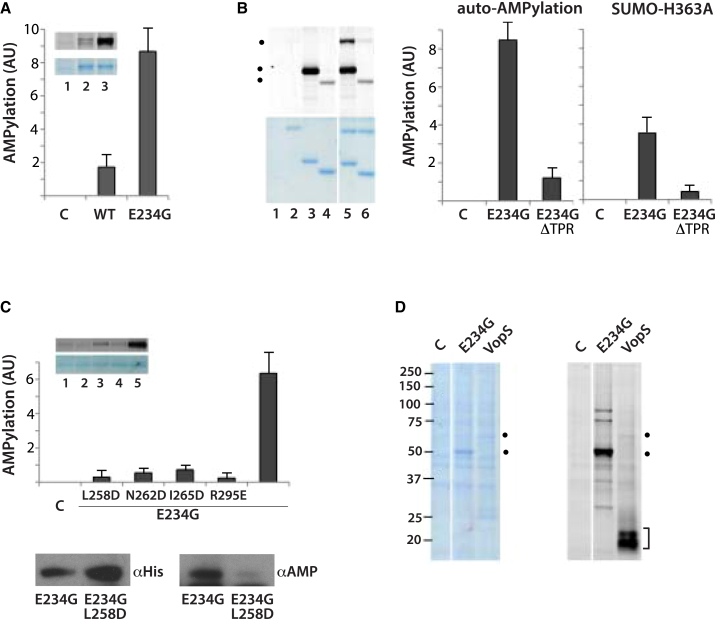
(A) Effect of E234G mutation on autoAMPylation of HYPE was analyzed by Yn-6-ATP-based assay, using WT and E234G variant (E234G) of HYPE (residues 103–434). For the control lane (C), HYPE protein was not included. Inset shows protein bands resolved by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie stained (bottom) and corresponding in-gel fluorescence (top). Fluorescence corresponding to autoAMPylation was quantified using ImageJ.
(B) Effect of deletion of TPR-motifs on AMPylation activity of HYPE was analyzed as in (A), using E234G (E234G, residues103–445) and E234G/ΔTPR (E234G, residues 172–445) variants of HYPE. In addition to autoAMPylation, AMPylation of H363A HYPE, containing SUMO-tag (SUMO-H363A, residues 103–445) was also analyzed. Left panel shows protein bands (bottom) and corresponding fluorescence (top). Lanes 1–6 correspond to; control without enzyme (1), SUMO-H363A (2), E234G (3), E324G/ΔTPR (4), E234G with SUMO-H363A (5), and E234G/ΔTPR with SUMO-H363A (6). Positions of AMPylated bands are indicated (.).
(C) Top panel shows effect of L258D, N262D, I265D, and R295E mutations on autoAMPylation of E234G HYPE (E234G, residues 172–445), analyzed as described in (A); inset shows protein bands (bottom) and corresponding fluorescence (top). Bottom panels show western blots of the full-length HYPE variants E234A and E234A/L258A, expressed in HEK293T cells, performed using either anti-His tag (αHis) (left) or anti-AMPThr (αAMP) antibodies (right).
(D) AMPylation of cellular proteins in vitro was performed using purified HYPE E234G (E234G, residues 103–445) and VopS in the presence of the cell lysate from HeLa cells. The cell lysate without added enzyme was used as a control (C). Left panel shows protein bands and the right panel corresponding fluorescence; autoAMPylation of HYPE E234G and VopS are indicated (.), as well as AMPylation in the area corresponding to mobility of small GTPases (]).
The indicated error bars in (A)–(C) represent SD from two experiments. See also Figure S7.