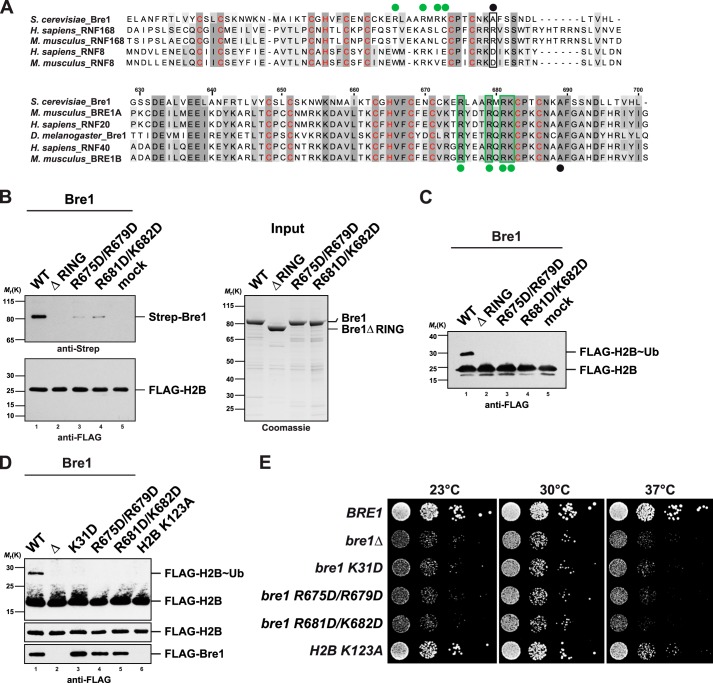
FIGURE 6.
Bre1 RING domain uses a basic region for nucleosome recognition. A, multiple sequence alignment of the RING domains of S. cerevisiae Bre1 compared with the RNF168 and RNF8 E3 ligases. Zinc-coordinating residues are labeled in red. Upper alignment, black dot indicates position of a basic residue in human RNF168 that is critical for histone interaction (Arg-57). Note that RNF8 is inactive toward H2A and has a negatively charged residue at this position. Lower alignment, comparison of Bre1 orthologs shows a stretch of highly conserved basic residues labeled with green dots. Black dot corresponds to the position of Arg-57 in RNF168. The basic Bre1 residues are not conserved in the H2A ubiquitin ligase RNF168 (green dots in upper alignment). Alignments were generated with ClustalW and colored in Jalview. Numbers indicate residues of S. cerevisiae Bre1. B, Bre1 RING domain directly interacts with the nucleosome. In vitro binding assay with NCPs immobilized on anti-FLAG beads and recombinant Bre1 constructs added to it in a 1:5 molar ratio. Proteins bound to the beads were eluted with FLAG peptide and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with an anti-Strep antibody to detect Strep-Bre1 and an anti-FLAG antibody to confirm equal loading of H2B. Mock indicates omission of Bre1 protein. Gel on the right shows input of Bre1 constructs. C, standard NCP ubiquitination assay was performed with the indicated Bre1 mutants (18 μm) and analyzed by anti-FLAG immunoblotting. Bre1 was omitted from mock sample. D, analysis of global histone H2B ubiquitin levels. BRE1 was deleted in a strain carrying FLAG-tagged histone H2B and then transformed with plasmid-based versions of wild-type FLAG-BRE1, empty vector, and the indicated mutants (lanes 1–5). A FLAG-H2B K123A strain containing genomic wild-type BRE1 (untagged) serves as a control (lane 6). Cell lysates were subject to anti-FLAG immunoprecipitation. Recovered proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using an anti-FLAG antibody. Lower FLAG-H2B panel shows a shorter exposure of the blot membrane. As FLAG-Bre1 was poorly detectable in whole cell extracts, FLAG-Bre1 that co-precipitated together with FLAG-H2B on the beads served as an approximate measure of protein stability/expression. E, growth analysis of wild-type BRE1 and mutant strains used in D. Growth was followed on SDC-HIS-URA plates (−HIS to maintain the FLAG-H2B plasmid, −URA to maintain FLAG-BRE1). Cell density was normalized, and 10-fold serial dilutions were prepared and then plated. Plates were incubated for 2–3 days at 23, 30, and 37 °C.