FIGURE 1.
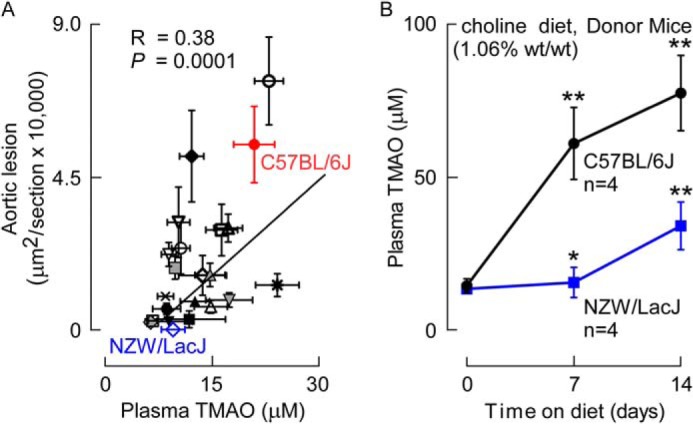
Aortic lesion area and plasma TMAO levels are positively associated across multiple inbred strains of mice. A, atherosclerotic plaque and plasma TMAO levels were determined in female F1 progeny from the cross between C57BL/6 mice homozygous for the human Apob transgene and 22 distinct inbred strains of mice (Table 1) as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Each data point represents the mean ± S.E. of lesion area and terminal plasma TMAO level within each strain, with Spearman correlation across all strains shown. Inbred strains with markedly divergent atherosclerosis susceptibility and TMAO levels selected to serve as cecal microbe donors included the atherosclerosis-prone (large lesion and high plasma TMAO) C57BL/6J (red) and atherosclerosis-resistant (small lesion and low plasma TMAO) NZW/LacJ (blue) strains. The key for symbols, along with mean ± S.E. values for atherosclerosis area and TMAO levels in each strain, are found in Table 1. B, confirmation that selected donor strains, C57BL/6J and NZW/LacJ, demonstrate markedly different TMAO plasma levels on a choline-supplemented diet. Selected donor strains were placed on the choline-supplemented (1.06%, w/w) diet, and plasma TMAO levels were quantified at the indicated times (n = 4/group at each time point). *, p < 0.05 and **, p < 0.01 for comparison with baseline (prior to choline diet) plasma TMAO level in each inbred strain.
