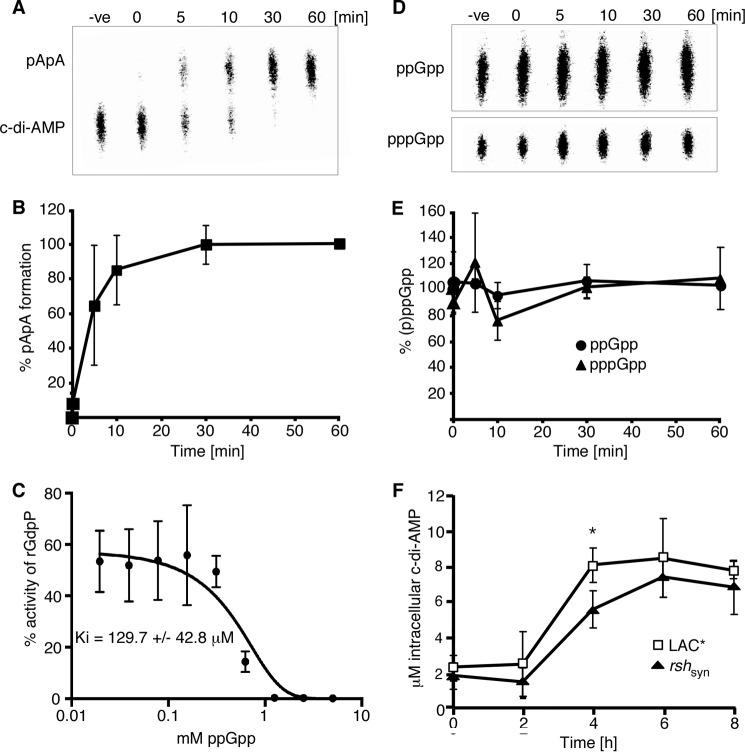
FIGURE 5.
Interplay between (p)ppGpp and c-di-AMP. A, phosphodiesterase activity of rGdpP protein against c-di-AMP. Enzyme reactions were set up in assay buffer containing 1 μm rGdpP and 20 μm c-di-AMP. Reactions were stopped at the indicated time points and analyzed by TLC. B, quantification of phosphodiesterase activity of rGdpP against c-di-AMP. Enzyme reactions were set up as described in A, and pApA production was quantified. The % pApA formation was calculated, and the average value and standard deviations from three independent experiments were plotted. C, in vitro phosphodiesterase activity of GdpP in the presence of ppGpp. Enzyme reactions were set up with 1 μm rGdpP, 20 μm radiolabeled c-di-AMP and ppGpp at concentrations ranging from 0 to 5 mm. The hydrolysis of c-di-AMP to pApA was monitored by TLC, and the percentage of pApA reaction product was quantified using ImageQuantTL. The average values and standard deviations of three independent experiments were plotted, and the data were fitted using a dose response inhibition algorithm in GraphPad Prism with the corresponding Ki value given. D, phosphodiesterase activity of rGdpP protein against (p)ppGpp. Enzyme reactions were set up in assay buffer containing 1 μm rGdpP and 20 μm (p)ppGpp. Reactions were stopped at the indicated time points and analyzed by TLC. E, quantification of phosphodiesterase activity of rGdpP against (p)ppGpp. Enzyme reactions were set up as described in D and ppGpp and pppGpp were quantified. The average value and standard deviations of the remaining amount of ppGpp and pppGpp in % from three independent experiments are plotted. F, intracellular c-di-AMP levels. The intracellular concentration of c-di-AMP in S. aureus LAC* and LAC*rshsyn was determined as described in Fig. 1C.