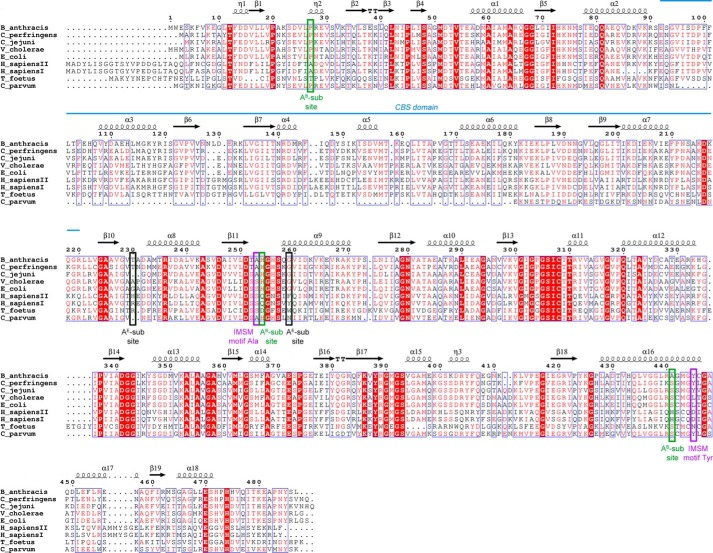
FIGURE 2.
Multiple sequence alignment of selected bacterial and eukaryotic IMPDHs. Identical residues are highlighted in red, and similar residues are shown as red letters. Secondary structure elements derived from BaIMPDH (PDB code 3TSB (11)) are depicted as arrows (representing β-strands) and coils (representing α- and 310-helices). The location of tandem CBS domains is shown as a blue line. Positions of two residues forming the IMSM are marked as purple rectangles. Positions of residues involved in binding of the NAD+ adenosine moiety in bacterial (AB-subsite) and eukaryotic (AE-subsite) enzymes are indicated by green and black rectangles, respectively. The sequences used in the alignment include B. anthracis str. Ames (gi: 30253523), C. perfringens (gi: 110800169), C. jejuni subsp. jejuni (gi: 15792385), V. cholera O1 biovar (gi: 15640786), E. coli str. K-12 (gi: 388478544), H. sapiens I (gi: 217035148) and H. sapiens II (gi: 66933016), T. foetus (gi:28373644), and C. parvum (gi: 323510309). The alignment was generated using MultiAlin (53) and ESPript (54) programs.