FIGURE 9.
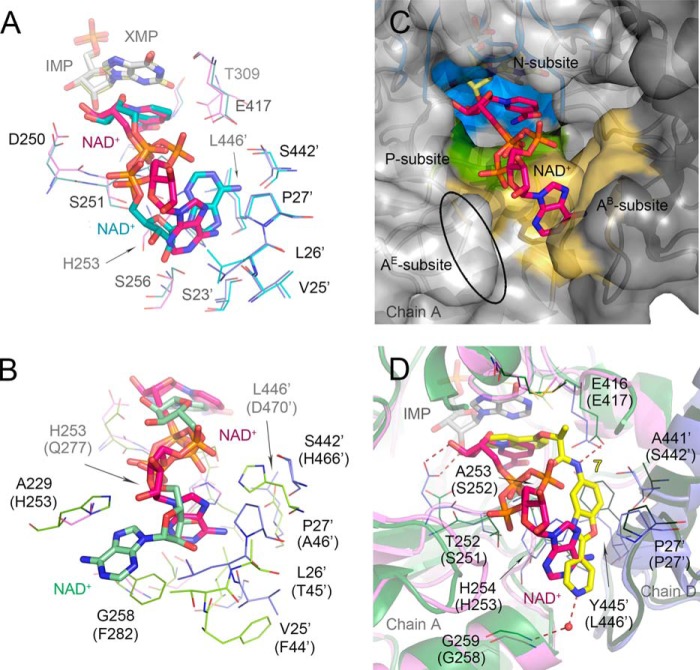
Different mode of NAD+ binding in bacterial IMPDHs. A, overlay of the cofactor position in VcIMPDHΔL·XMP·NAD+ and VcIMPDHΔL·IMP·NAD+. Only ligands (depicted as sticks) and the interacting residues (represented as lines) are shown. Color code is as follows: for XMP/NAD+ structure as in Fig. 7; for IMP/NAD+ structure, chain B (teal), symmetry-generated adjacent chain (light blue), NAD+ (teal), IMP (gray). Water molecules and hydrogen bonds are omitted for clarity. B, overlay of the cofactor position in VcIMPDHΔL·IMP·NAD+ and hIMPDH2·CPR·NAD+ (PDB code 1NFB, as in Fig. 1B). Only the cofactors (depicted as sticks) and the interacting residues (represented as lines) are shown. Variable residues are labeled according to VcIMPDH numbering with hIMPDH2 numbering in parentheses. IMP and CPR are omitted for clarity. Color code is as follows: for VcIMPDHΔL as Fig. 7; for hIMPDH2, chain A (green), symmetry-generated adjacent chain (lime), NAD+ (pale green). C, migration of the cofactor A-subsite to the adjacent monomer. Chains A (light gray) and symmetry-generated adjacent chain (dark gray) are shown in a surface representation. XMP (light yellow) and NAD+ (magenta) are shown as sticks. Three NAD+ subsites N- (blue), P- (green), and the bacterial AB-subsite (orange) are represented. The ellipsoid depicts the localization of the eukaryotic AE-subsite. D, overlay of the cofactor and inhibitor positions in VcIMPDHΔL·XMP·NAD+ and BaIMPDHΔL·IMP·7. Color code for the cofactor structure as in Fig. 7. Residues (shown as lines) are labeled according to BaIMPDH numbering with VcIMPDH numbering in parentheses. Chains A (green) and D (dark green) of BaIMPDHΔL·IMP·7 are shown in a cartoon representation. IMP (light gray), NAD+ (magenta), 7 (yellow) are shown as sticks. Hydrogen bonds are depicted as red dashed lines. Water molecule for the inhibitor is shown as a red sphere. Waters molecules for the cofactor structure are omitted for clarity.