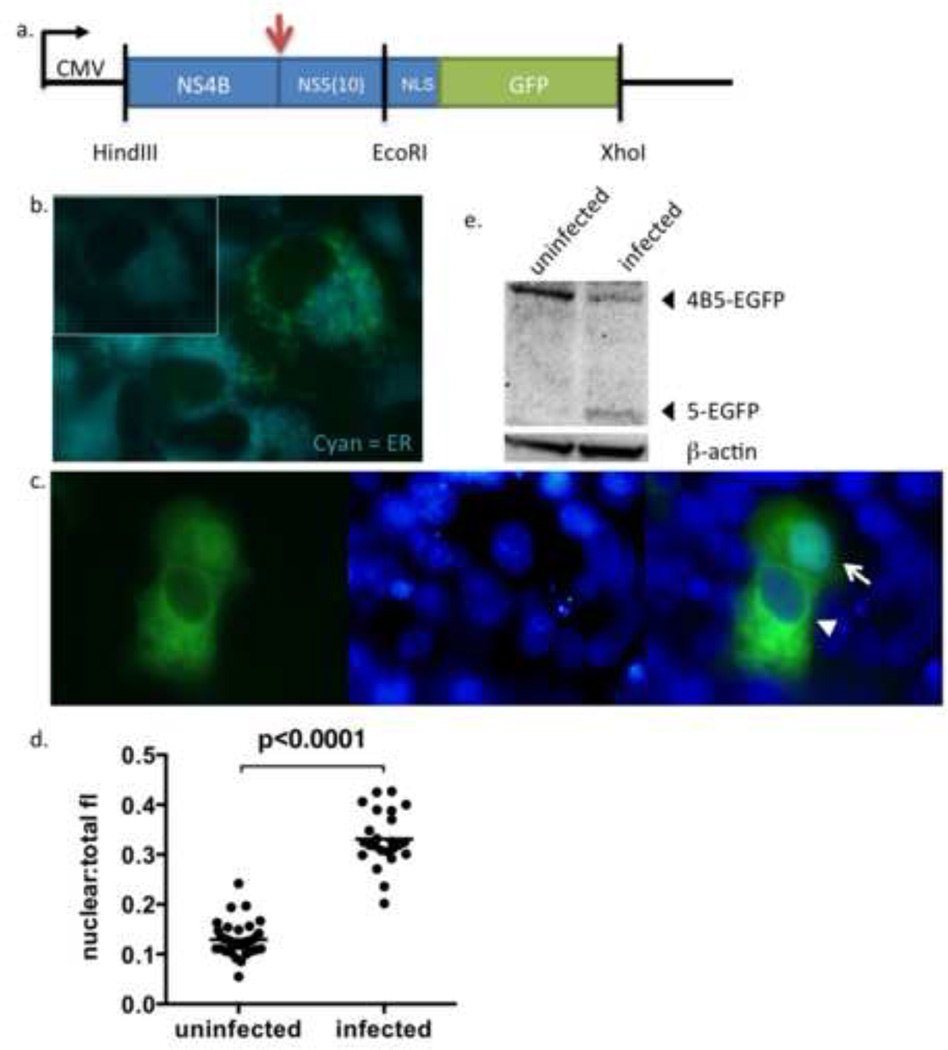
Figure 1. Construction and characterization of p4B5-EGFP.
(a) Schematic of the p4B5-EGFP construct containing NS4B and the first 30 nucleotides of NS5 of the DENV-2 genome tagged with the SV40 NLS and eGFP. The arrow indicates the cleavage site utilized by the DENV NS2B3 protease. The vertical lines represent restriction endonuclease sites.
(b) Unfixed Vero cells transfected with p4B5-EGFP were stained with ER-Tracker Blue-White DPX dye (Cyan) 24hrs post-transfection and immediately imaged to detect colocalization of NS4B5-EGFP (reporter, green) with ER membranes (blue, magnification, ×100). Inset reflects ER staining of cells alone. (c) Unfixed Vero cells transfected with p4B5-EGFP were infected with DENV-2 16681. Nuclei were counterstained with NucBlue for live cells (Invitrogen) (blue) to detect nuclear localization of GFP (green, magnification, ×100). Cytoplasmic expression of GFP is indicated by the arrowhead and nuclear expression of GFP is indicated by an arrow (magnification, ×100). (d) Analysis of nuclear to total fluorescence intensity ratios of GFP (nuclear:total fl) in uninfected and DENV infected cells at 24 h was performed using ImageJ software. Each symbol represents analysis of a single cell. Statistical analysis was performed using nonparametric Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney rank sum test. Straight line represents the median. (e) Cellular lysates were prepared 24 h post infection and subjected to Western blotting for GFP or β-actin. The 5-EGFP fragment represents the cleavage product resulting from cleavage between NS4B and NS5-EGFP during viral infection.