Figure 5.
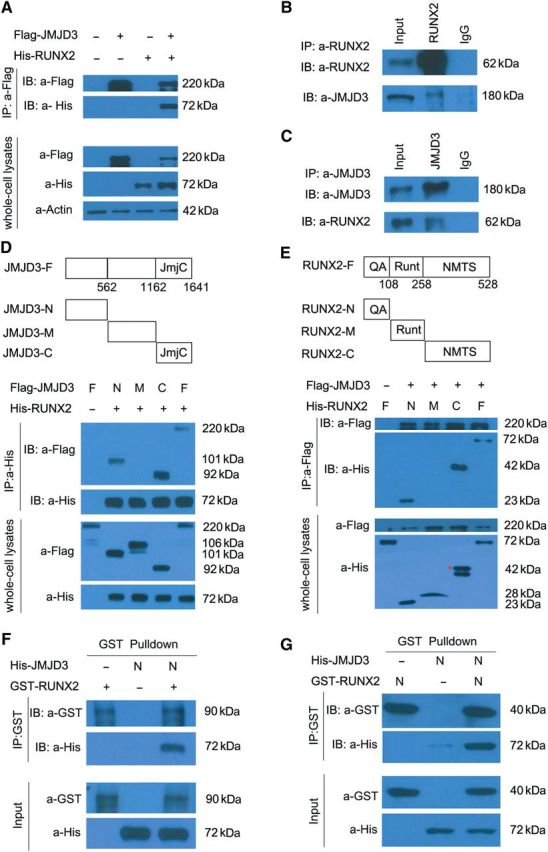
JMJD3 biochemically interacts with RUNX2. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of His-RUNX2 with Flag-JMJD3 in transiently transfected HEK293T cells. Immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed with an anti-Flag antibody, and RUNX2 proteins were detected by immunoblot (IB) analysis with anti-His antibody. IB of whole-cell lysates without immunoprecipitation was used to detect protein expression throughout experiments. (B) Co-IP of endogenous JMJD3 with RUNX2 in the primary culture of chondrocytes of E14.5 limbs. IP was performed with anti-RUNX2 antibody. JMJD3 proteins were detected by IB assay with anti-JMJD3 antibody. (C) Co-IP of endogenous RUNX2 with JMJD3 in the primary culture of chondrocytes from E14.5 embryos. IP was performed with anti-JMJD3 antibody, and RUNX2 proteins were detected by IB assay with anti-RUNX2 antibody. (D and E) Co-IP of constructs as indicated co-expressed in 293T cells. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-His antibody (D) or anti-Flag antibody (E), followed by IB with an anti-Flag antibody and anti-His antibody. Red asterisk indicates the correct size of His-RUNX2-C proteins. JmjC, Jumonji C domain. QA, glutamine/alanine rich domain. Runt, runt homology domain. NMTS, nuclear matrix targeting signal. (F and G) GST-pulldown experiments with bacterially expressed GST-RUNX2 (F) or GST-RUNX2-N (G) and in vitro transcribed/translated JMJD3-N as indicated. The above experiments were repeated at least three times.
