Figure 6.
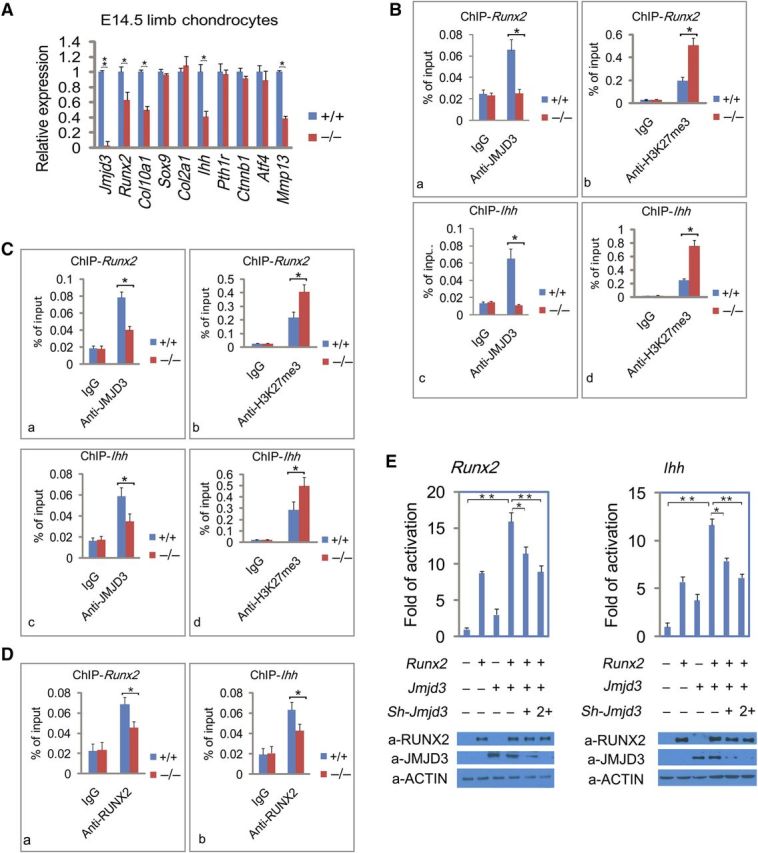
JMJD3 cooperates with RUNX2 to regulate Runx2 and Ihh transcription. (A) RT-qPCR analysis to determine the expression levels of chondrocyte-specific genes relative to Gapdh in limb chondrocytes of WT and Jmjd3–/– mice at E14.5. (B) ChIP-qPCR assays with antibodies specific for JMJD3 (a, c) or H3K27me3 (b, d,) at the promoters of Runx2 (a, b) and Ihh (c, d) in WT and Jmjd3−/− primary chondrocytes. (C) ChIP-qPCR assays with antibodies specific for JMJD3 (a, c) or H3K27me3 (b, d) at the promoters of Runx2 (a, b) and Ihh (c, d) in WT and Runx2−/− primary chondrocytes. (D) ChIP-qPCR assays with antibodies specific for RUNX2 at the promoters of Runx2 (a) and Ihh (c) in WT and Jmjd3−/− primary chondrocytes. (E) Luciferase reporter assays. ATDC5 chondrocytes were transfected with the pGL3-basic reporter containing 2 kb Runx2 promoter (a) or 2 kb Ihh promoter (b) with or without lentiviral expression vectors encoding Runx2, Jmjd3, or Jmjd3-shRNA (sh-Jmjd3) as indicated. The basal luciferase activity for each reporter was calculated as 1 in y-axis. Western blots show levels of expressed proteins in the lysates of transfected cells (bottom). The above experiments were repeated three times. Positions of primers (B, D, and E) in the promoters of Runx2 and Ihh for ChIP-qPCR experiments were showed in Supplementary Figure S5Ba–c. Signals were shown as the percentage of the input. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, two-tailed Student's t-test. Error bar represents the SE of three independent experiments.
