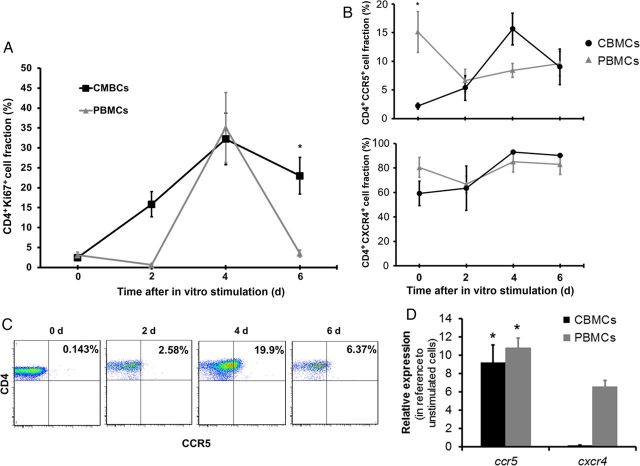
Figure 3.
CCR5 expression upon in vitro stimulation and proliferation is increased in CD3+CD4+ cord blood mononuclear cells (CBMCs) to levels similar to those in adult peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). A, Fractions of CD4+Ki67+ cells were determined in CBMCs and PBMCs over time following in vitro stimulation with phytohemagglutinin (PHA)/interleukin 2 (IL-2). Data shown are expressed as the mean ± standard error (SE) of 12 cord blood and 8 adult blood samples. B, The fraction of CD4+CCR5+ and CD4+CXCR4+ after stimulation with PHA/IL-2 in CBMCs and PBMCs. Data shown are expressed as the mean ± SE of 12 cord blood and 8 adult blood samples. C, Representative dot plots showing the fraction of CD4+CCR5+ T cells after in vitro simulation with PHA/IL-2 in CBMCs. Data shown are dot plots of 1 representative donor of 12. D, Unstimulated and stimulated purified CD4+ CBMC and PBMC messenger RNA levels were measured after 24 hours by real-time polymerase chain reaction to determine the relative expression of CCR5 and CXCR4. Data shown are expressed as the mean ± SE of triplicate samples from 6 donors. *P < .001, compared with PBMCs (A and B) or unstimulated cells (D) at the corresponding time point.