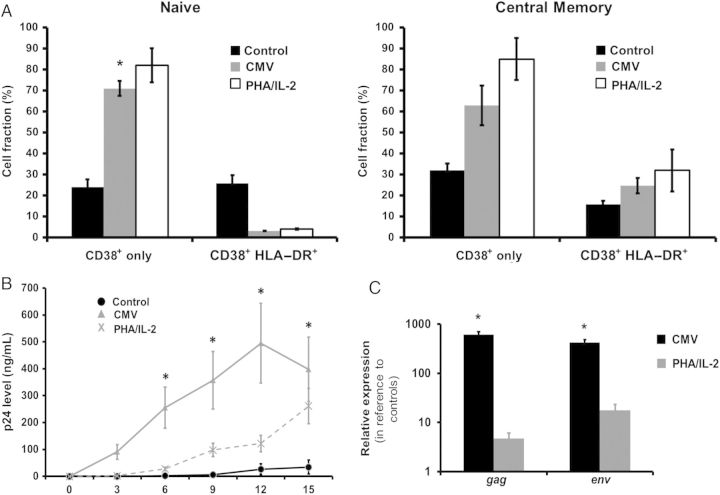
Figure 6.
Expression of activation markers on T central memory (TCM) cord blood mononuclear cells (CBMCs) may correlate with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) susceptibility. A, The fraction of CD4+ naive T (TN) cells and TCM CBMCs that express CD38 with or without HLA-DR was determined on day 4 after coculture with cytomegalovirus (CMV)–infected macrophages, uninfected macrophages (control), or phytohemagglutinin (PHA)/interleukin 2 (IL-2). Data shown are expressed as the mean ± standard error (SE) of samples from 8 individual donors. Purified CD4+ CBMCs were infected by HIV-1BaL after coculture with CMV-infected macrophages, uninfected macrophages (control), or PHA/IL-2. B, HIV-1 replication was measured in the cell supernatants over time by detection of HIV-1 p24 viral antigen, using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Data shown are expressed as the mean ± SE of samples from 8 individual donors. C, Messenger RNA levels were measured 6 days after infection by real-time PCR to determine the relative expression of env and gag. Data shown are expressed as the mean ± SE of samples from 8 individual donors. *P < .001, compared with control CBMCs at the corresponding time point.