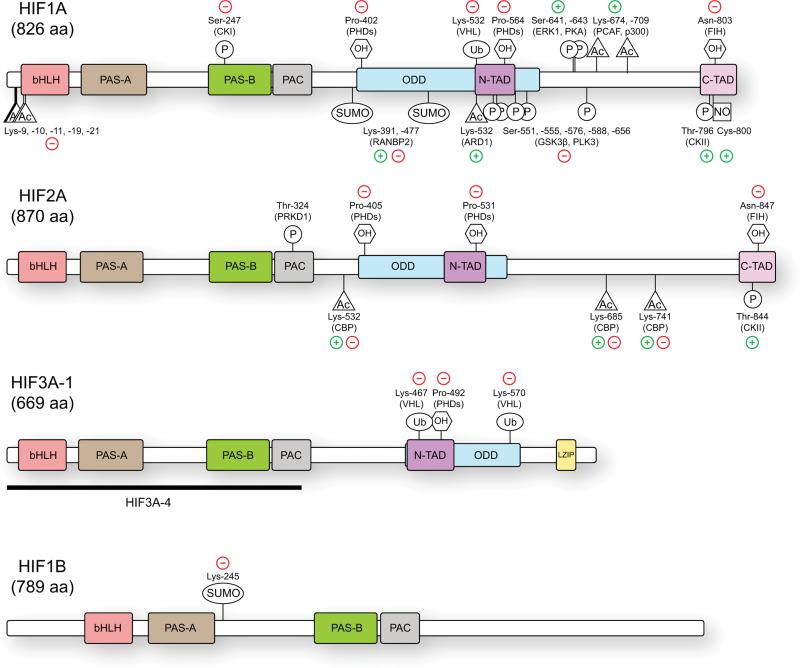
Figure 1.
HIF protein domains and post-translational modifications. The HIF proteins are comprised of several conserved domains that are involved in DNA binding (basic Helix-Loop-Helix, bHLH), protein-protein interactions and dimerization (PER-ARNT-SIM, PAS-A, PAS-B, and PAS-associated C-terminal domain), oxygen-dependent degradation (ODD) and transcriptional activation (N-TAD, C-TAD). Numerous HIF3A isoforms exist, with several longer forms possessing transactivation and leucine zipper (LZIP) domains (HIF3A-1) while others lack any known transactivation domains and act as negative regulators (HIF3A-4). Multiple post-translational modifications are known to modulate HIF protein stability and transcriptional activity. Selected modifications are shown here along with the enzyme responsible and the overall positive (+) or negative (−) effects on HIF transcriptional function.