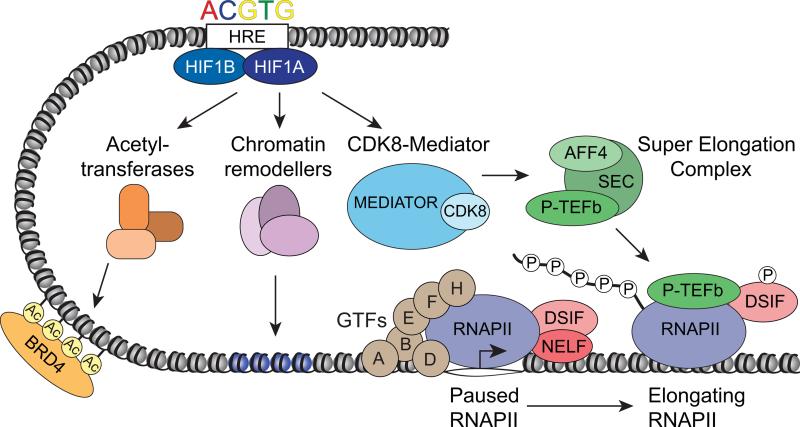
Figure 3.
A model of HIF1A-dependent transactivation. During normoxia, almost all HIF1A target genes display an open chromatin environment and harbor transcriptionally active but paused RNA polymerase II (RNAPII). Upon stabilization by hypoxia, HIF1A dimerizes with HIF1B and binds to the permissive HREs of these target genes. HIF1A then recruits various coactivators including acetyl-transferases and chromatin remodelers as well as CDK8-Mediator along with the Super Elongation Complex (SEC) containing AFF4 and P-TEFb. These events result in increased histone acetylation and BRD4 binding and the P-TEFb-triggered release of paused RNAPII into productive elongation. Importantly, without CDK8, HIF1A is still able to bind to the HRE and induce histone acetylation but fails to recruit Mediator and the SEC or to stimulate RNAPII elongation.