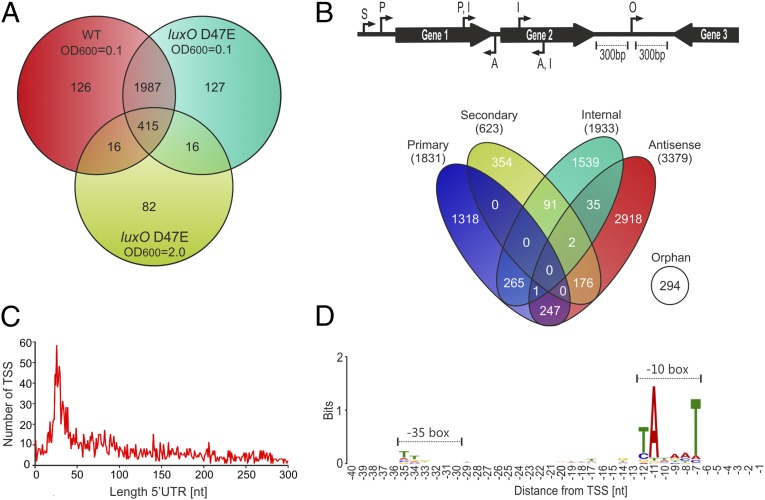
Fig. 1.
Expression profiling and TSS mapping of wild-type and luxO D47E V. cholerae. (A) Venn diagram of differentially expressed genes in the wild-type and luxO D47E V. cholerae C6706 strains at LCD (OD600 of 0.1) and HCD (OD600 of 2.0). Numbers of cDNA reads for annotated genes were compared to wild-type cells at HCD (OD600 of 2.0). Statistically significant genes (P < 0.05) that changed >1.5-fold are shown. (B) Identification and classification of TSSs in V. cholerae. A total of 7,240 TSSs were identified by dRNA-seq and classified according to their genomic locations (Top). A, antisense; I, internal; O, orphan; P, primary; S, secondary. (C) Length distribution of 5′ UTRs in V. cholerae. For each primary and secondary TSS, the distance to the cognate translation initiation site was calculated and the frequency of each 5′ UTR length was plotted. (D) Consensus motif for V. cholerae promoters. DNA sequences from −40 to +1 upstream of the 7,240 TSSs were analyzed for conserved sequence elements using the MEME tool.