Fig. 4.
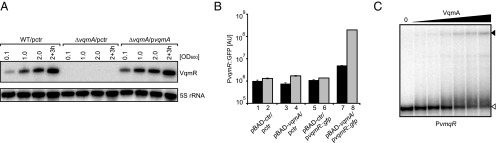
VqmA activates vqmR transcription. (A) Total RNA was obtained for wild-type/pctr, ΔvqmA/pctr, and ΔvqmA/pvqmA V. cholerae strains at the indicated times during growth. The Northern blot was probed for VqmR. The 5S rRNA served as loading control. (B) GFP production from a vqmR transcriptional reporter was measured in E. coli carrying the indicated plasmids following 12 h growth in LB with 0.2% (final concentration) glucose (black bars) or 0.2% (final concentration) l-arabinose (gray bars). Error bars represent SD of three replicates. (C) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) showing that VqmA protein binds the vqmR promoter sequence. Migration of the [32P] end-labeled vqmR promoter fragment in the absence and presence of increasing concentrations of purified VqmA::3XFLAG protein (indicated by the black triangle above the gel) was determined by native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and autoradiography. The open triangle indicates free DNA; filled triangle indicates DNA in complex with VqmA::3XFLAG. A negative control consisting of a mutated version of the vqmR promoter is shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S5C.
