Fig. 6.
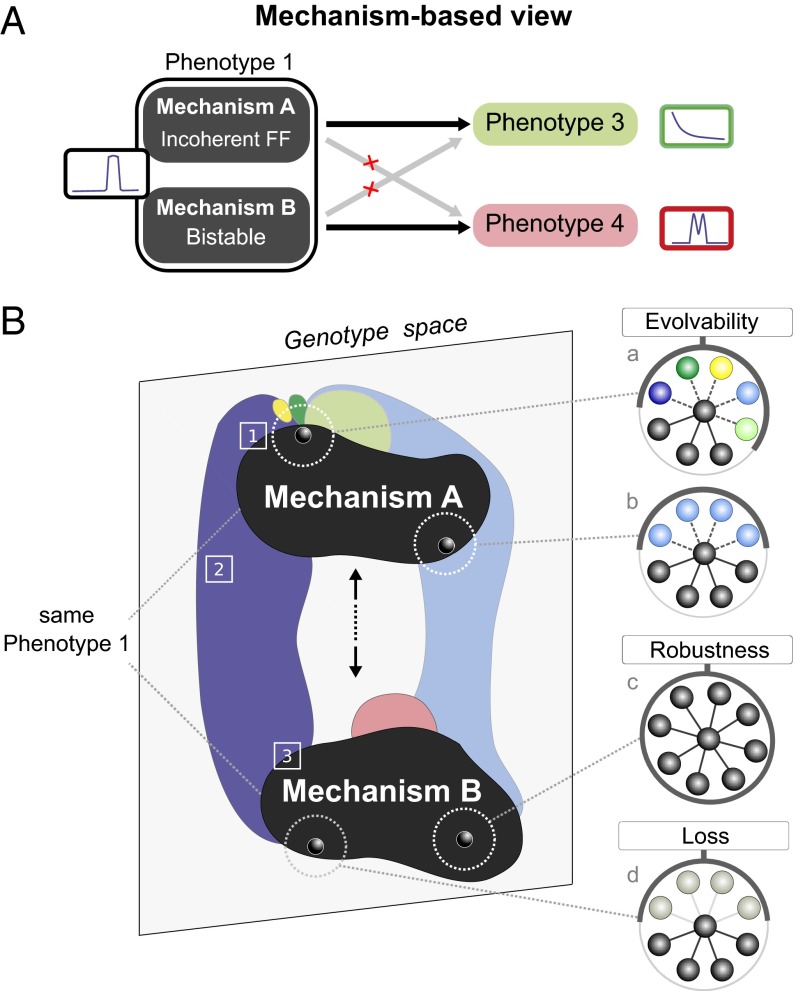
Mechanism-based view on evolvability. (A) Distinct mechanisms to achieve a common phenotype have access to distinct phenotypes: the Gradient phenotype appears exclusively accessible from mechanism A (Bistable or Overlapping Domains) as is Double Peak from mechanism B (Incoherent feed-forward or Mutual Inhibition). (B) Main features of genotype space: existence of phenotypic hubs [1], ubiquitously accessible phenotypes [2], and continuous phenotypic transitions [3]. Four phenotypic neighborhoods are shown as representative cases of either potentially evolvable genotypes (found close to the edge of the neutral space: a, b, and d) or completely robust genotypes (internal: c).