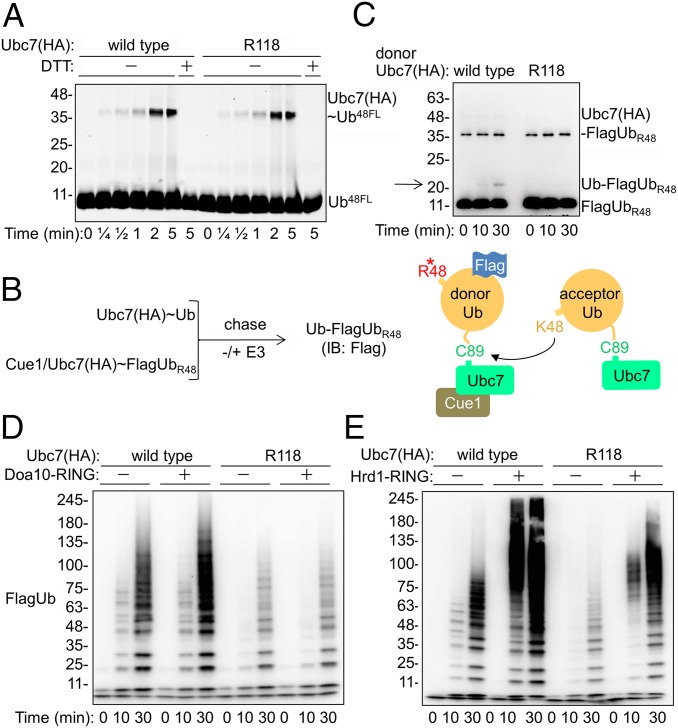
Fig. 2.
The reduced catalytic activity of Ubc7R118 is partially rescued by the Hrd1 RING domain. (A) Kinetics of Ubc7∼Ub thioester formation. The Ubc7:Cue1 dimer was incubated with E1 and Ub48FL for the indicated time periods at 30 °C. Proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE with or without DTT, after which fluorescence was detected using a Typhoon reader (GE Healthcare). (B, Left) Flowchart for single-round Ub-turnover experiments. Ubc7 and the Ubc7:Cue1 dimer were charged separately with Ub and FlagUbR48, respectively, in the presence of E1 and ATP. Both reactions were terminated by the addition of Apyrase to deplete ATP. Equal volumes of each reaction then were mixed for further incubation with either buffer or an E3 ligase; then diUb (Ub–FlagUbR48) formation was determined by immunoblot analysis with anti-Flag Abs. (Right) Graphic depiction of the single-round Ub-turnover reaction. (C) Rates of Ub–FlagUbR48 formation by Ubc7 and Ubc7R118, determined in a single-round Ub-turnover assay in the absence of E3. The E2∼Ub thioesters were combined and incubated at 30 °C for the indicated time periods. The reaction was terminated by the addition of SDS sample buffer. Ubiquitylated proteins were resolved by SDS/PAGE and visualized by immunoblot analysis with anti-Flag Abs. Arrow indicates the position of diUb. (D and E) Activation of polyUb chain formation by E3 RING domains. Either Ubc7 or Ubc7R118 was incubated in an ubiquitylation reaction mixture, as described in Materials and Methods in the presence of equal amounts of recombinant Doa10 or Hrd1 RING domains. Ub chains were resolved by SDS/PAGE and visualized by an immunoblot analysis with anti-Flag Abs.