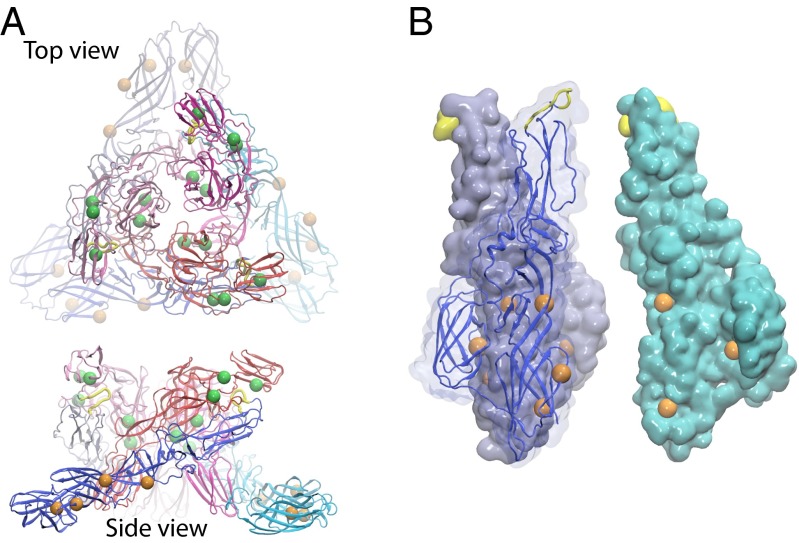
Fig. 5.
Locations of pH-sensitive residues on (A) the (E2–E1)3 viral spike complex in the M state and (B) the (E1)3 in the HT state. Strictly conserved pH-sensitive residues that contribute to the M→FI and FI→HT steps are mapped in green and orange beads, respectively, on the alphaviral spike. Two nonstrictly conserved residues with ΔΔG > 1 kcal/mol in the M→FI and FI→HT steps are shown in smaller beads. In B, one of the E1 monomers (cyan) is displaced and rotated to show the residues on the trimeric interface inside the HT.