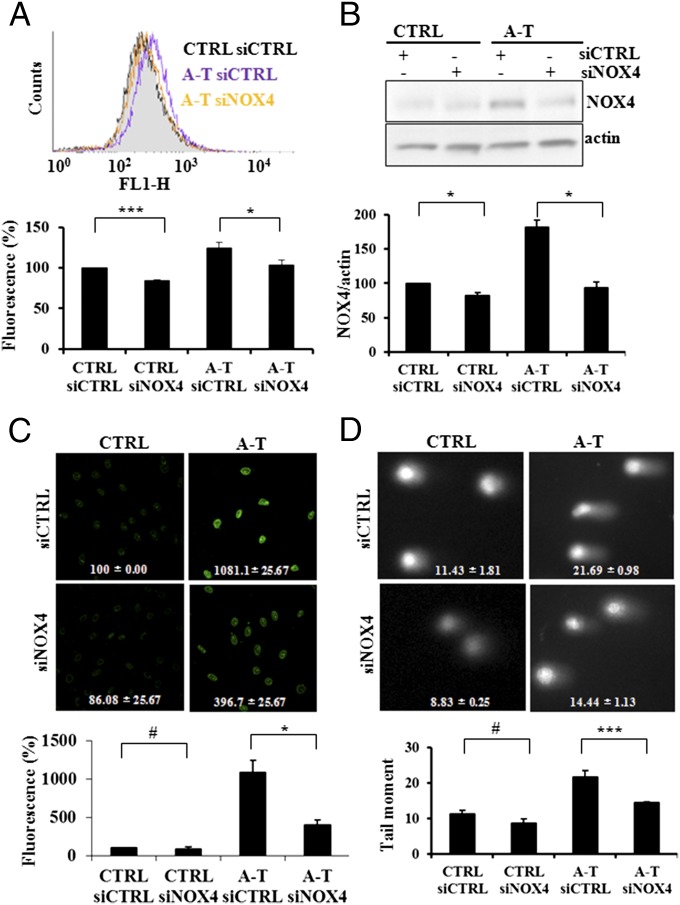
Fig. 2.
NOX4 inactivation by siRNA reduces ROS and DNA damage. (A) A-T cells (A-T) exhibited elevated ROS levels compared with control cells (CTRL), levels which were reduced when the cells were treated with NOX4 siRNA (Upper, raw DCF fluorescence; Lower, quantification). (B) A-T cells (A-T) exhibited elevated NOX4 levels compared with controls cells (CTRL), levels which were reduced when the cells were treated with NOX4 siRNA (Upper, immunoblot; Lower, quantification). (C) NOX4 silencing by siRNA reduces 8-OH deoxyguanosine levels in A-T primary fibroblasts (A-T) (Upper, images of control (CTRL) and A-T cells treated with siCTRL and siNOX4 RNAs and stained for 8-OH deoxyguanosine; bottom, quantification). (D) Oxypurine levels were elevated in A-T cells (A-T) compared with controls (CTRL) and reduced in A-T cells (A-T) treated with siNOX4 (Upper). Fpg-specific lesions detection by comet assay (representative images). (Lower) Quantification. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.001; #, nonsignificant.