Fig. 1.
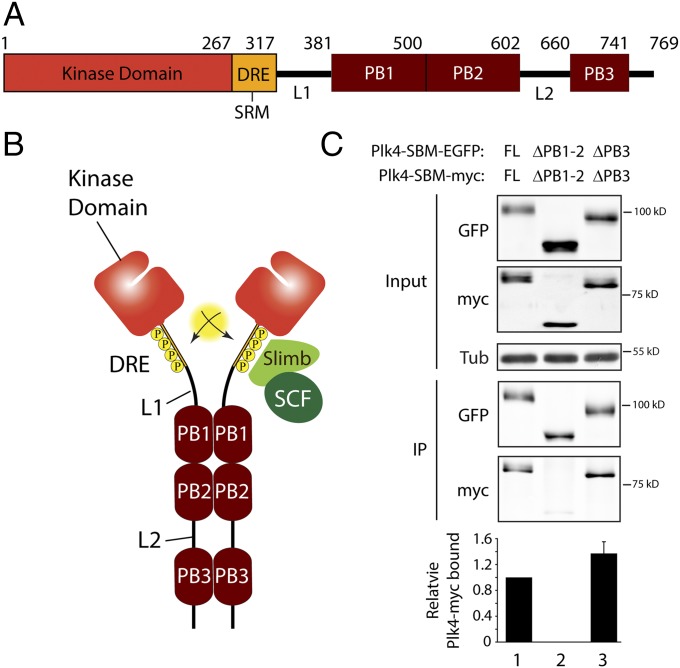
Tandem Polo boxes PB1 and PB2 are required domains for Plk4 homodimerization. (A) Linear map of the Drosophila Plk4 polypeptide showing functional and structural domains including PB1–3, the DRE [containing the SRM (Slimb recognition motif)], L1, and L2. (B) Model of Plk4 autodestruction. Homodimerization facilitates trans-autophosphorylation, generating an extensive phosphodegron within each DRE. The SCFSlimb/β-TrCP Ubi-ligase binds the phosphodegron and ubiquitinates Plk4, targeting it for proteasomal degradation. (C) Anti-GFP immunoprecipitates (IPs) were prepared from lysates of S2 cells transiently co-overexpressing the indicated inducible nondegradable SBM EGFP and myc-tagged Plk4 constructs. Blots of the input lysates and IPs were probed for α-tubulin, GFP, and myc. Error bars indicate SEM. Amounts of Plk4-EGFP and associated Plk4-myc in the IPs were determined by densitometry of the anti-GFP and myc immunoblots and then normalizing the measurements with the amounts of SBM-Plk4 present in the IPs. The plotted values are relative to the coimmunoprecipitation in lane 1.