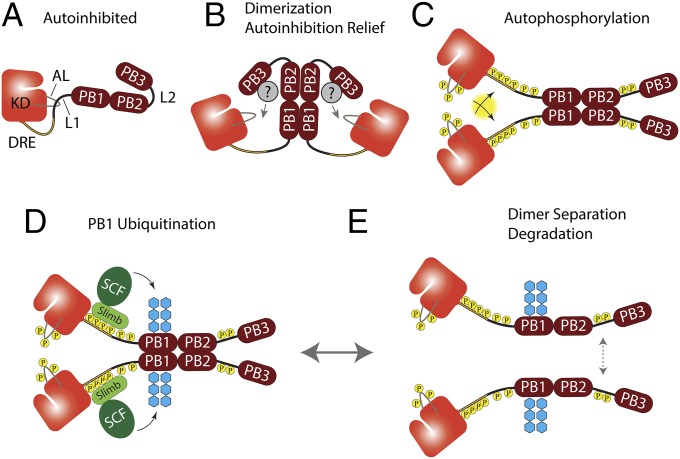
Fig. 7.
Speculative multistep model for Plk4 activation and regulation. (A) Newly synthesized Plk4 is initially autoinhibited, allowing homodimer formation via PB1–PB2 interaction. (B) PB3 relieves autoinhibition by positioning an unidentified binding partner to move L1 away from the AL. (C) Plk4 autophosphorylates several domains with assorted consequences; our data do not mandate an order of phosphorylation. (1) AL phosphorylation fully activates the kinase; (2) trans-autophosphorylation of the DRE generates the Slimb-binding phosphodegron; (3) L1 phosphorylation further relieves autoinhibition; (4) L2 phosphorylation promotes dimer separation. (D) SCFSlimb is recruited and ubiquitinates PB1 (blue hexagons). (E) Kinase activity promotes dimer separation through L2 phosphorylation and additional unidentified residues. We propose that dimer separation causes the disassembly of higher-order Plk4 complexes.