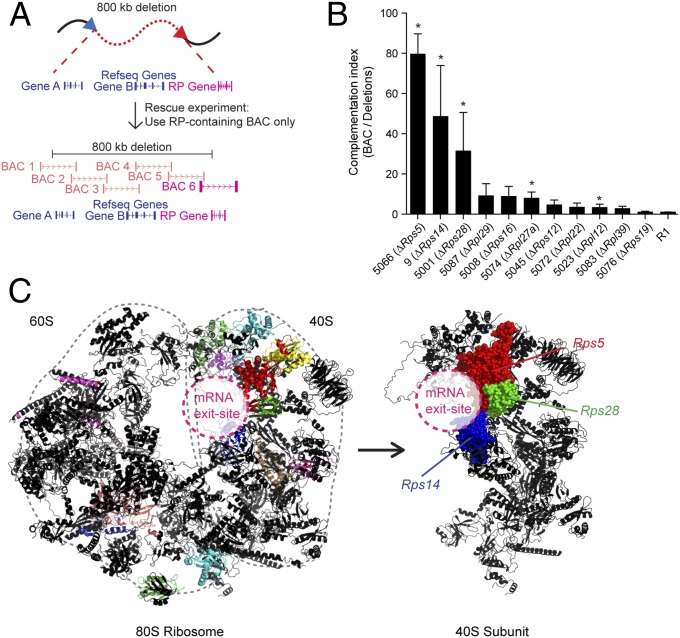
Fig. 2.
Complementation experiments reveal a site-specific role for RP genes. (A) Design of BAC complementation experiments. The backbone of a BAC vector containing the affected RP gene was modified using puromycin-, hygromycin-, or zeocin-resistance genes and was transfected into DelES clones of interest lacking one copy of the corresponding RP gene. (B) Complementation experiments of RP-deleted clones. Clones with a single RP gene deletion are shown. (See Fig. S3 for all values in the bar graph.) The complementation index was obtained by dividing relative EB numbers (based on primary clone values) of BAC-transfected clones by those of mock-transfected clones. Error bars show SEM of at least two independent experiments. (C) The RP-deleted clones that showed the best BAC complementation (farthest left columns in B) are colocalized at the mRNA exit site of the 40S ribosomal subunit (PDB ID codes 3U5E, 3U5F, and 3U5G) (26, 27).