Fig. 1.
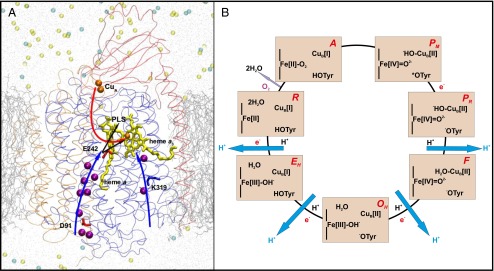
(A) A three-subunit (SU) CcO. SU I (blue), II (red), and III (orange) are displayed as transparent ribbons. The D and K channels of proton transfer are marked with blue arrows. Crystallographic water molecules present in these proton channels are shown in purple. Electron transfer (red arrow) takes place from CuA (orange) via heme a (yellow) to the binuclear center comprising heme a3 (yellow)–CuB (orange). Protons are transferred from Glu242 (E242) either to the PLS or to the binuclear center (black arrows). Lipid bilayer (silver lines), water (gray dots), and sodium (light yellow) and chloride (cyan) ions are also displayed. (B) The catalytic cycle of CcO. The states of heme a3, CuB, and the cross-linked tyrosine are displayed. Each light orange rectangle corresponds to a state of the BNC, the name of which is displayed in red (Upper Right). Pumped protons are shown in blue, black H+ indicates uptake of a proton for water formation, and e− indicates transfer of an electron from the low-spin heme a. Catalysis of O2 reduction occurs clockwise.
