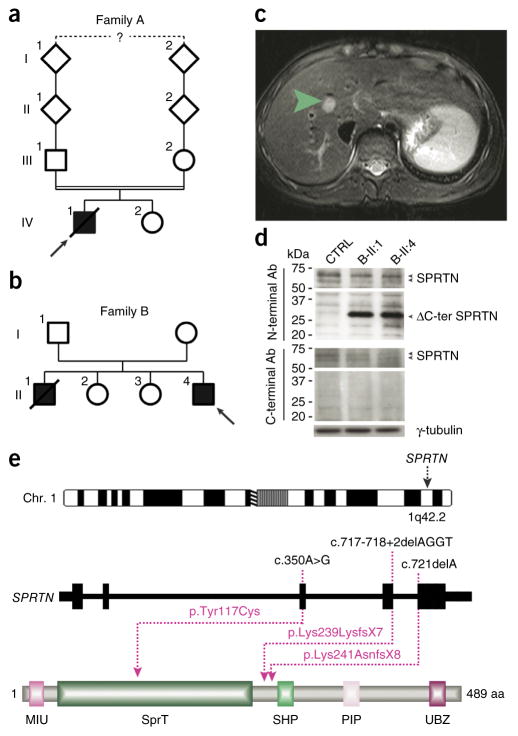
Figure 1.
Identification of causative SPRTN mutations. (a,b) The pedigrees of families A and B. Filled and open symbols denote affected and healthy individuals, respectively; an arrow indicates the index patient, and diagonal lines indicate deceased status. The double line shows parental consanguinity, and the question mark denotes that the exact degree of consanguinity is unknown. (c) Axial view of magnetic resonance imaging of the liver of patient B-II:4. The green arrow indicates a 12 mm × 13 mm lesion mass with an absence of arterial phase enhancement within segment VIII of the liver that was subsequently shown to be a HCC. (d) Analysis of total cell extracts of patients’ LCLs with SPRTN antibodies (Ab) raised against the N- or C-terminal part of the protein. (e) Genomic localization and protein structure of SPRTN. The genomic structure is based on the longest ORF containing five coding exons (black rectangles). The positions of the identified mutations are shown at both the gene (top) and protein (bottom) levels. The protein diagram depicts the predicted functional domains of SPRTN. aa, amino acids.