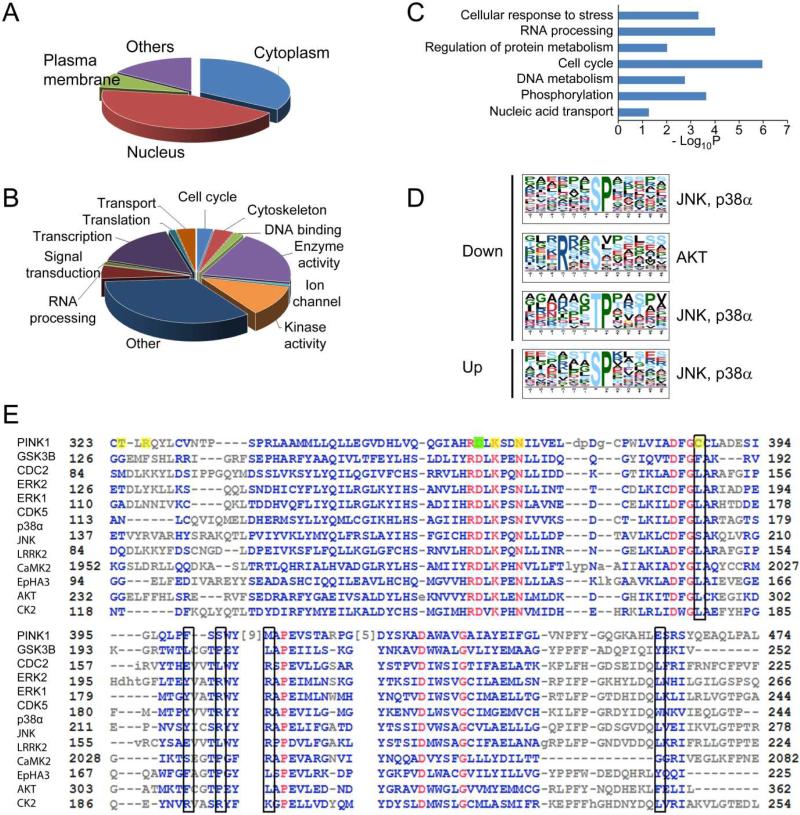
Fig. 6.
Bioinformatics analysis of phosphorylation events. Gene Ontology analysis of changed phosphoproteins in two categories, (a) cellular localization and (b) biological function, indicates an enrichment of nuclear proteins, and proteins involved in DNA and RNA metabolism. (c) Pathway analysis indicates a significant over-representation of proteins in several pathways including cell cycle and cellular response to stress. (d) Motif analysis of the phosphopeptides with altered phosphorylation identified proline-directed kinase recognition motif, which was recognized by JNK, p38α, and Akt. (e) Alignment of PINK1 with that of many kinases both proximal and distal to PINK1 in the kinome tree, the sequence that covers substrate recognition residues is used for the alignment. The proton acceptor (D362) was labeled with a filled green box, and the rest of the substrate interacting residues including ATP binding sites were labeled with filled yellow boxes. The open black boxes indicates proposed +1 proline interacting residues.