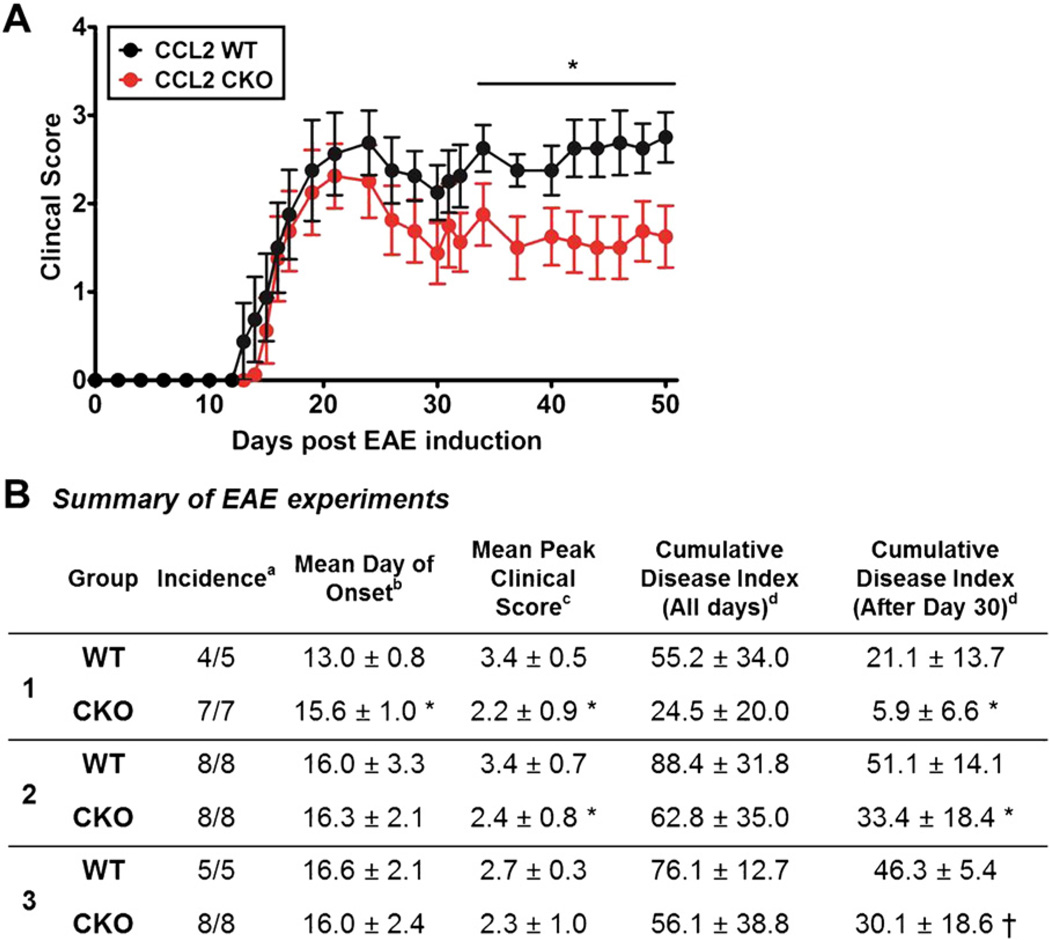
Fig. 3.
Astrocyte CCL2 CKO, as compared to WT littermates, has less severe EAE late in disease. A, Astro-CCL2-CKO mice had significantly better clinical EAE scores late (after EAE day 30) compared with CCL2 WT mice. *p < 0.05 (repeated-measures ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni pairwise analysis). Graphical representation of experiment #2 from Table. B, Table showing clinical assessments in three separate experiments. Statistical analysis shows significant decrease in the cumulative disease score index after 30 days of EAE induction in astro-CCL2-CKO compared to CCL2 WT. aIncidence is the number of mice that developed EAE signs from the total number of mice in each group. bMean day (±SEM) of onset was assessed when mice showed first clinical disease signs (score of >1) after EAE induction. cMean peak clinical score (±SEM) was assessed when each mouse reached its maximum clinical score. dCumulative disease index (±SEM) was calculated by summing the daily clinical scores of each mouse and averaging them within each group. “All days” signifies day 0 of EAE induction to day of sacrifice, while “After Day 30” is from day 30 of EAE to day of sacrifice. *p < 0.05, †p < 0.08 versus CCL2 WT (mean ± SEM).