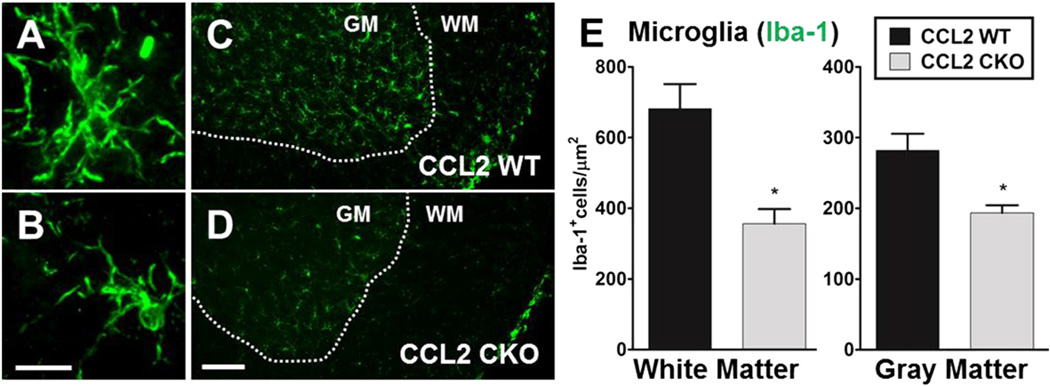
Fig. 6.
Selective deletion of CCL2 from astrocytes results in less microglial activation diffusively in the spinal cords during EAE. Representative immunofluorescence image of A, ramified/activated and B, resting microglial cell using Iba-1 staining (green). Scale bar, 10 µm. C and D, astro-CCL2-CKO mice show a reduced number of ramified/activated microglial cells in white matter (WM) and gray matter (GM) of the spinal cord compared to CCL2 WT mice during EAE. Scale bar, 100 µm. E, Quantitative analysis confirms that astro-CCL2-CKO mice have reduced activated microglial cells in the white and gray matter of the spinal cord during EAE. *p < 0.05 versus CCL2 WT (mean ± SEM).