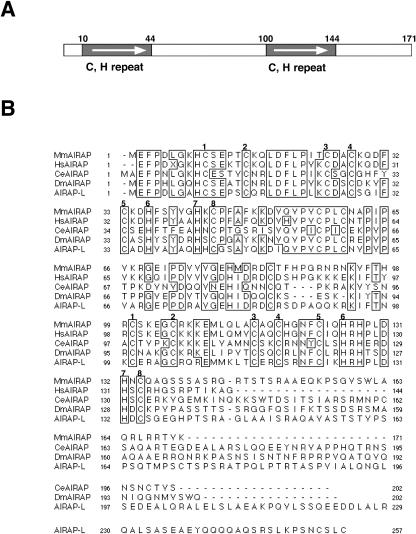
Fig 5. Cross-species conservation of AIRAP amino acid sequences (A) Diagram of the primary structure of the predicted gene product of murine AIRAP. The two 34-residue repeats containing the invariant cysteines and histidines are indicated (“C, H repeat”). (B) Alignment (Higgins and Sharp 1988)of AIRAP sequences from Mus musculus (Mm), Homo sapiens (Hs, AI659863), C elegans (Ce, Z81555), Drosophila melanogaster (Dm, AI134276) and an AIRAP- like human gene (AIRAP-L, AA449622). Sequences for human and fly genes are from ESTs, while sequences for mouse and C elegans are from full-length cDNAs and genomic clones. The 8 invariant cysteine and histidine residues that form the internal repeat in the protein are indicated by numbers above the alignment. Residues identical in at least 4 of the 5 protein sequences are boxed

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.