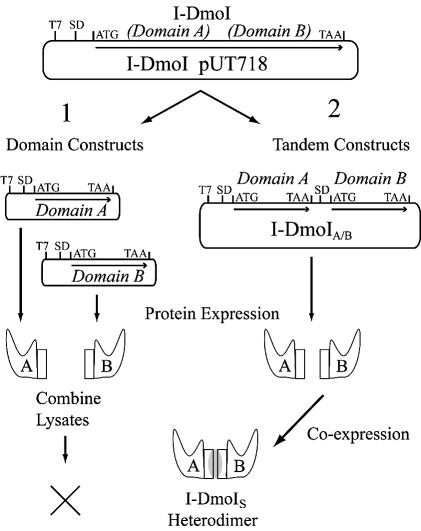
Figure 5.
Creating a functional heterodimer. The wild-type I-DmoI plasmid was used as the template in efforts to create I-DmoIS via two pathways as shown. T7, promoter region; SD, Shine–Dalgarno sequence; ATG and TAA are the start and stop codons, respectively. Coding regions are indicated by arrows. (1) Domain constructs: individual A and B domain expression vectors were created. Protein expression was carried out separately for each domain and then lysates were combined and tested for heterodimer formation based on DNA cleavage activity. No active constructs were generated by this method. (2) Tandem constructs: individual A and B domain coding sequences were cloned into a single plasmid and co-expressed under the control of a single T7 promoter. Constructs were tested for heterodimer formation based on DNA cleavage activity as described in Table 4, Figure 6 and the text.