Figure 7.
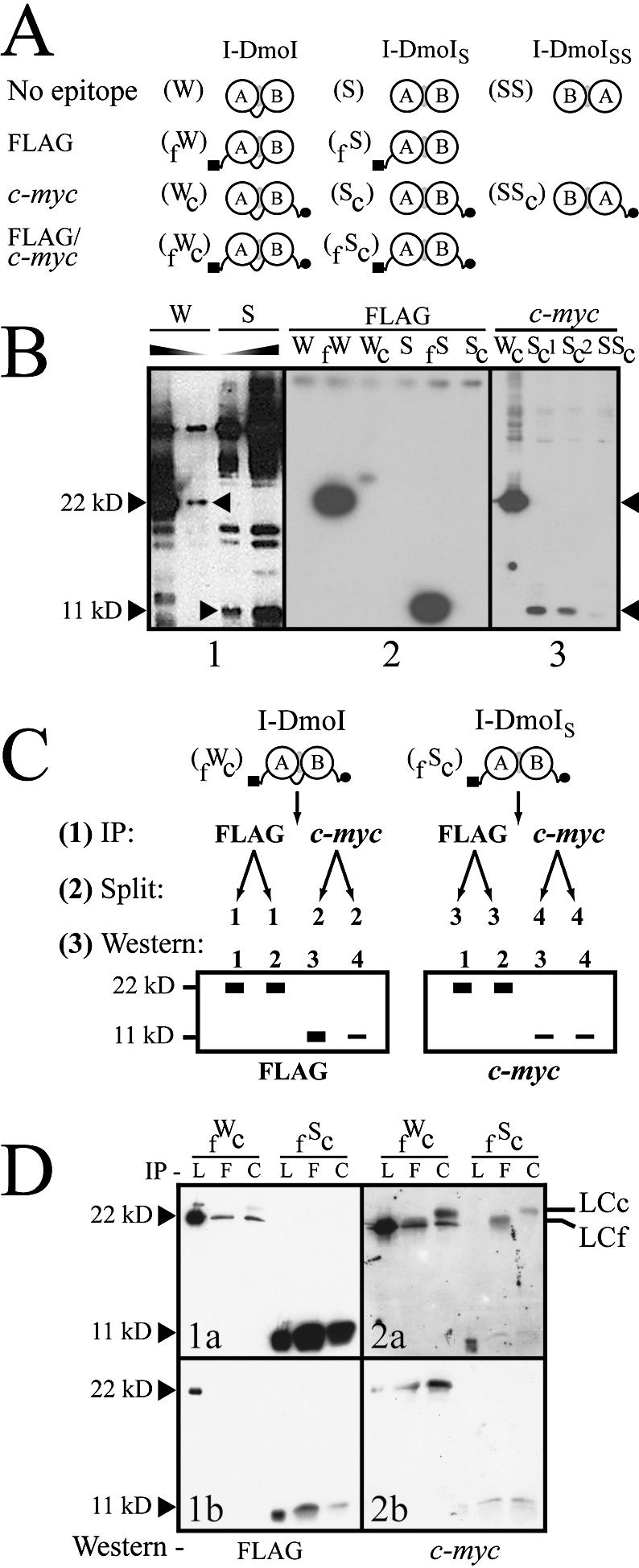
The extent of heterodimer formation in I-DmoIS. (A) Schematic of the I-DmoI constructs used to probe heterodimer formation. I-DmoI constructs were created with the N-terminal FLAG (black square) and/or C-terminal c-myc (black circle) epitopes. Abbreviations for construct names appear in parenthesis to the left of each diagram. (B) Western blots quantifying I-DmoI and I-DmoIS. For all panels, sizes indicate expected position of wild-type I-DmoI (22 kDa) and split constructs (11 kDa; I-DmoIS and I-DmoISS). Panel 1 shows that I-DmoIS does not contain detectable full-length protein using anti-I-DmoI polyclonal antibody. Shaded triangles indicate decreasing protein concentration. Panel 2 shows that no cross-reactivity is evident for untagged or c-myc-tagged I-DmoI and I-DmoIS using the anti-FLAG antibody (the shadow band between lanes fW and Wc is an exposure artifact). Panel 3 shows the dramatically reduced amount of domain B in protein lysates (total protein amounts loaded are as in panel 2) when c-myc-tagged I-DmoI, I-DmoIS and I-DmoISS proteins were probed with anti-c-Myc antibody. Sc1 and Sc2 represent crude and cleared lysates of Sc protein, respectively. (C) Schematic of IP/western blot protocol. This method was used to determine relative dimerization. See text for details. (D) Western blot of dimerization. Results from the protocol outlined in (C). Panels 1a and 1b show different exposures of the same experiment; Panels 2a and 2b show the results of two separate experiments. Size markers are as in (B). IP indicates antibody used for immunoprecipitation: L, lysate-only control (no IP); F, anti-FLAG antibody; and C, anti-c-Myc antibody. Western indicates antibody used for western blot. By-products of the IP step: LCc, light chain of the anti-c-Myc antibody; LCf, light chain of the anti-FLAG antibody.
