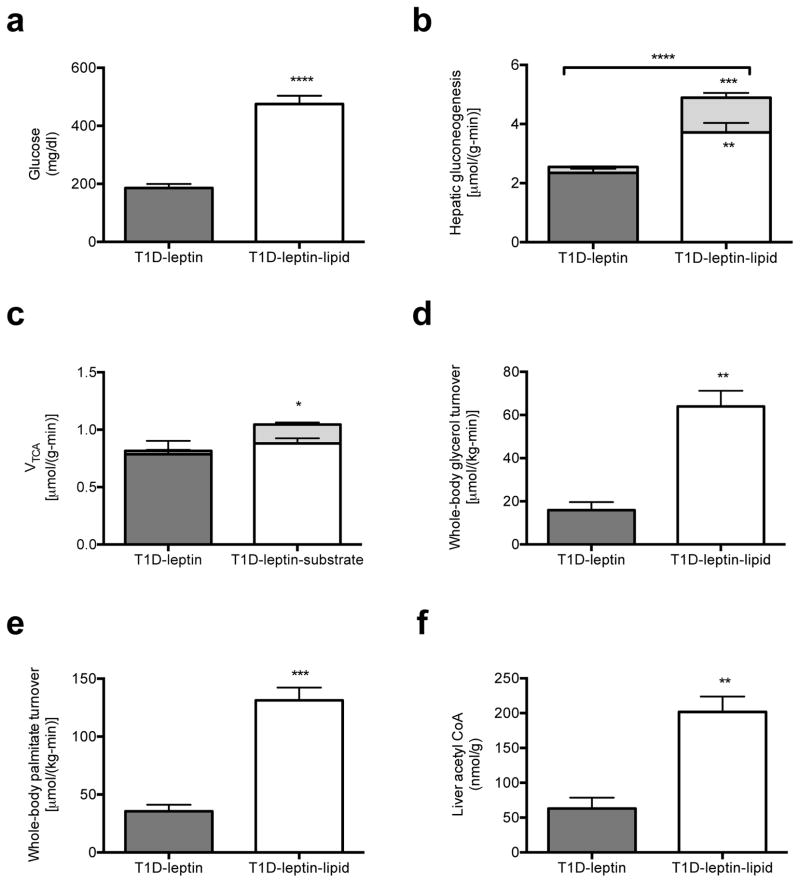
Fig. 3.
Substrate (Intralipid/heparin) infusion blocks leptin’s effect to suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis in T1D rats. (a) Fasting plasma glucose. (b) Hepatic gluconeogenesis from pyruvate (lower bars) and glycerol (upper bars). Gluconeogenesis from both pyruvate and glycerol was increased (P<0.01 and P<0.001, respectively) in lipid-infused rats. (c) VTCA from fatty acid oxidation (lower bars) and through pyruvate dehydrogenase (upper bars). VTCA through PDH was increased (P<0.05) in lipid-infused rats. (d), (e) Whole-body glycerol and palmitic acid oxidation. (f) Liver acetyl CoA concentration. In all panels, data are mean ± S.E. of n=6 per group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.