Figure 1. Cholesterol loading of VSMC leads to foam-cell formation, loss of VSMC characteristics, and emergence of macrophage-like features.
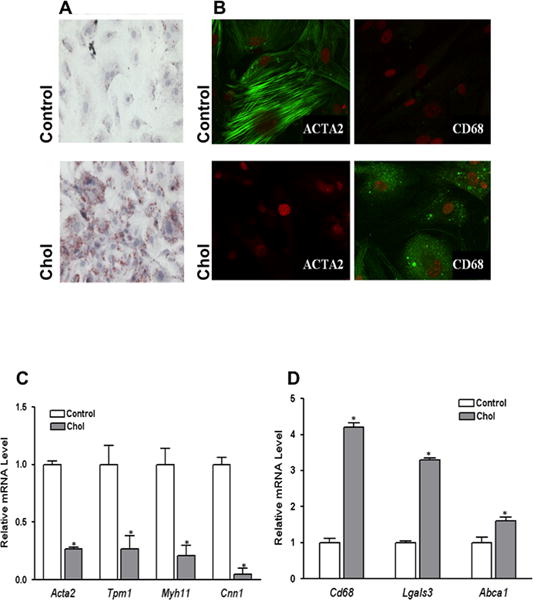
Subconfluent mouse aortic VSMC were treated with (Chol) or without (Control) cyclodextrin (CD)-cholesterol complexes in 0.2% BSA for 72 hours. After cholesterol loading cells assumed the appearance of foam cells with Oil Red O-stained lipid droplets (A). Immunostaining showed decreased protein levels of VSMC marker ACTA2, while macrophage marker CD68 was dramatically increased at the end of 72 hour cholesterol treatment period (B). Consistent changes to this phenotype shift are qRT-PCR analyses of VSMC (C) and macrophage marker (D) gene expression. Data shown are mean ± SD of triplicates of qRT-PCR reactions and are representative of two independent experiments.
