Figure 4. Maintaining MYOCD expression prevents and reverses phenotypic changes in VSMC associated with cholesterol loading.
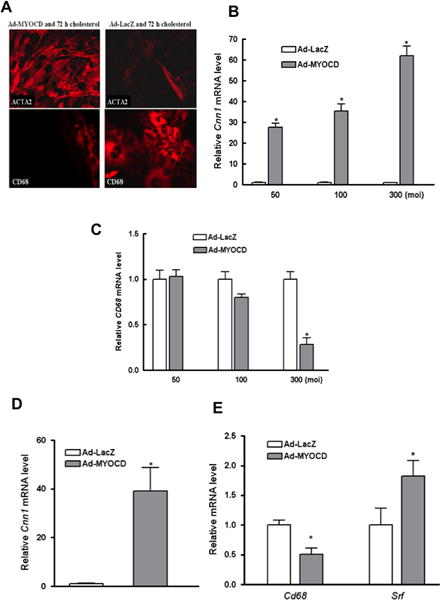
(A) Shown is immunostaining of mouse VSMC transduced with adenoviral vectors (MOI of 300) expressing either MYOCD (Ad-MYOCD) or LacZ (Ad-LacZ) prior to incubation with CD-cholesterol complexes for 72 hours (40×). Note the persistence of ACTA2 and the lack of CD68 in Ad-MYOCD vs. Ad-LacZ cells. (B–C) qRT-PCR analysis of mRNA from cells treated as in (A) showed an adenoviral vector-dose related maintenance and suppression, respectively, of VSMC marker Cnn1 and of macrophage marker Cd68. (D–E) Mouse VSMC were transduced with Ad-MYOCD or Ad-LacZ (MOI of 300) after 3 days of cholesterol loading. qRT-PCR results show increases of Cnn1 (D) and Srf mRNA (E), and suppression of Cd68 mRNA (E) in Ad-MYOCD cells (*p < 0.05; data shown are mean ± SD of triplicates of qRT-PCR reactions and are representative of two independent experiments).
