Figure 3.
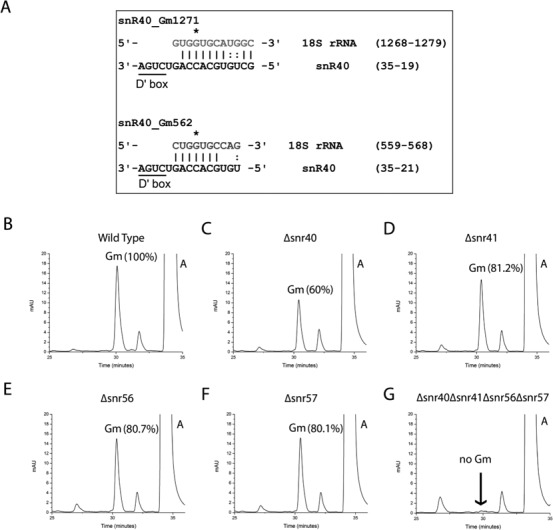
Sequence and RP-HPLC analysis of the C/D box snoRNAs for the identification of snoRNA involved in Gm562. To identify snoRNA involved in the methylation of Gm562, we reanalyzed methylation guide sequences involved in assigning substrate specificity to the C/D box snoRNPs of all already known C/D box snoRNAs. (A) Our sequence analysis revealed the likelihood of snR40 to be the snoRNA involved in guiding methylation of Gm562 residue. Sequence analysis of the methylation guide sequence of snR40 shows significant complementarity to the region surrounding Gm562 in the 18S rRNA. Ribose methylated G is marked with star and is always five nucleotides upstream to the D/D′ box. We next checked the involvement of snR40 in the methylation of Gm562. Nucleoside composition of 18S rRNA isolated from snR40 deletion mutant was analyzed, and compared with the single deletion mutants of three other snoRNAs; snr41, snr56 and snr57. RP-HPLC chromatogram of WT (B), Δsnr40 (C), Δsnr41 (D), Δsnr56 (E) and Δsnr57 (F) demonstrated that where single deletions of snr41, snr56 and snr57 led only to 20% decrease in Gm amount compared to wild type 18S rRNA, deletion of snr40 led to 40% decrease in the Gm amount. This clearly indicated that loss of snr40 influences methylation of more than one Gm residues and supported involvement of snR40 in Gm562 methylation. (G) RP-HPLC chromatogram of the quadruple mutant (Δsnr40Δsnr41Δsnr56Δsnr57). Deletion of all four snoRNAs (snR40, snR41, snR56 and snR57) leads to complete loss of Gm residues from the 18S rRNA. Together with composition analysis of 18S rRNA from single deletion mutant, analysis with quadruple mutant further supported the involvement of snR40 in methylation of Gm562.
