Figure 6.
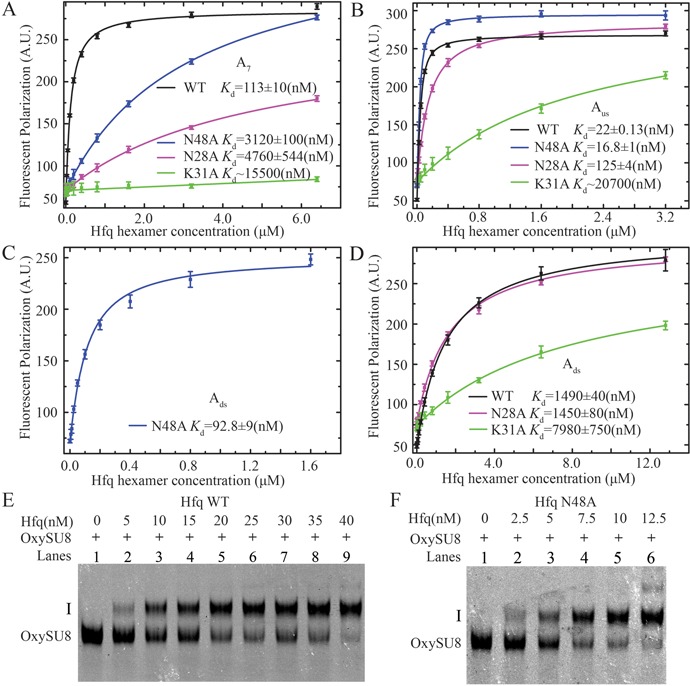
The effects of Hfq mutations (N28A, K31A and N48A) on RNA binding affinities. (A) N28A (magenta), N48A (blue) and K31A (green) mutations dramatically decrease the binding affinity for A7 to Hfq (compared with a Kd of ∼113 nM for wild-type Hfq; (19)). (B) The binding affinity of Aus RNA for N28A and K31A is both lower compared with that for wild type. In contrary, the N48A mutant exhibits higher affinity for Aus. (C) The N48A mutation dramatically increases the affinity for Ads (∼16-fold) compared with wild type. (D) The binding affinity Ads for the K31A mutant is significantly lower. The N28A mutation does not affect the binding of Ads. In EMSA assays, compared to wild-type Hfq (E), the N48A mutant caused a prominent mobility shift of full-length OxySU8 at lower concentrations (F).
