Figure 7.
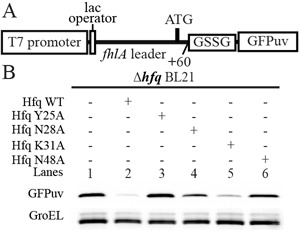
An appropriate RNA binding affinity is important for Hfq regulation in vivo. (A) A schematic diagram of the reporter system used for in vivo translation assays. The DNA sequence encoding the fluorescent protein GFPuv is fused to the leader sequence of fhlA and is thus under the regulation of OxyS and Hfq. The level of GFPuv expression in this system will consequently reflect the translation level of the mRNA with this fhlA leader. (B) Deletion of hfq increases the GFPuv expression level (lane 1) compared with wild-type Hfq (lane 2). GFPuv expression in the presence of the Y25A mutant (lane 3) is similar to that in the hfq− strain. Similarly, neither the N28A (lane 4) nor the K31A mutant (lane 5) was capable of suppressing GFPuv expression as wild-type Hfq. This finding is presumably due to the deficiency of these mutants in binding OxyS. The N48A mutant, which binds to OxyS more tightly than wild-type, also does not suppress the expression level of GFPuv (lane 6). GFPuv was stained with an anti-GFP antibody and GroEL was used as a loading control.
