Figure 2.
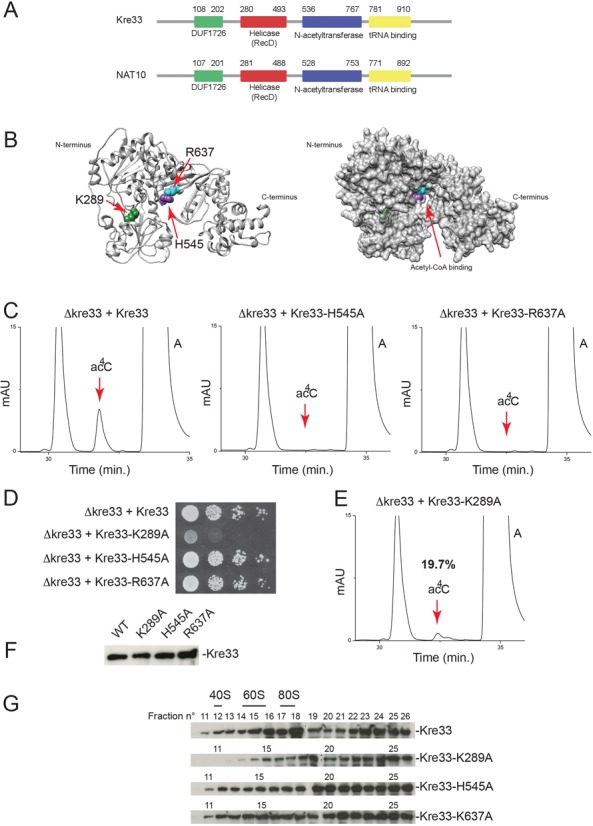
Yeast Kre33 is responsible for 18S rRNA acetylation and its helicase domain is required for efficient RNA modification. (A) Protein domain organization of yeast Kre33 and its human homolog NAT10: a conserved domain of unknown function (DUF1726) is flanked by a helicase domain (RecD), an acetyl-CoA binding domain (N-acetyltransferase) and a tRNA binding motif. (B) Left, ribbon representation of Kre33 (10–930) indicating residues mutated in this work. This model is based on PDB entry 2ZPA. Right: surface rendering highlighting the Acetyl-CoA binding pocket and residues shown to the left. (C) Mutating individual Kre33 residues lining the acetyl-CoA binding pocket leads to total loss of 18S rRNA acetylation. 18S rRNA purified from the indicated yeast strains was analyzed by HPLC for the presence of acetylation. (D) 18S rRNA acetylation is not essential to yeast cell growth in complete medium. Growth assay on plates, showing serial dilutions (1x to 103x from left to right) spotted on rich medium and incubated for 3 days at 30°C. (E) A functional Kre33 helicase domain is required for efficient 18S rRNA acetylation. 18S rRNA analyzed as in panel (C). (F) Metabolic stability of the protein constructs analyzed in this work. Identical amounts of total protein extracted from the indicated strains tested by western blotting with an anti-His antibody recognizing the tag present at the carboxy-terminal end of the constructs. (G) A functional Kre33 helicase domain is required for efficient association of the protein with pre-40S ribosomes. Total extracts of the yeast strains indicated were resolved on 10–50% sucrose gradients. Total protein was extracted from 26 fractions and tested by anti-His western blotting. Kre33 co-migrates with a large spectrum of pre-ribosomes, including early pre-90S precursors, detected in fractions heavier than 80S ribosomes (19 and above), as well as precursors of the small and large subunits (pre-40S and pre-60S), which migrate in fractions heavier than 40S (fractions 12–14) and 60S (fractions 15–17), respectively. The association of Kre33 with the pre-40S fraction is lost in the helicase-deficient mutant K289A.
