Figure 3.
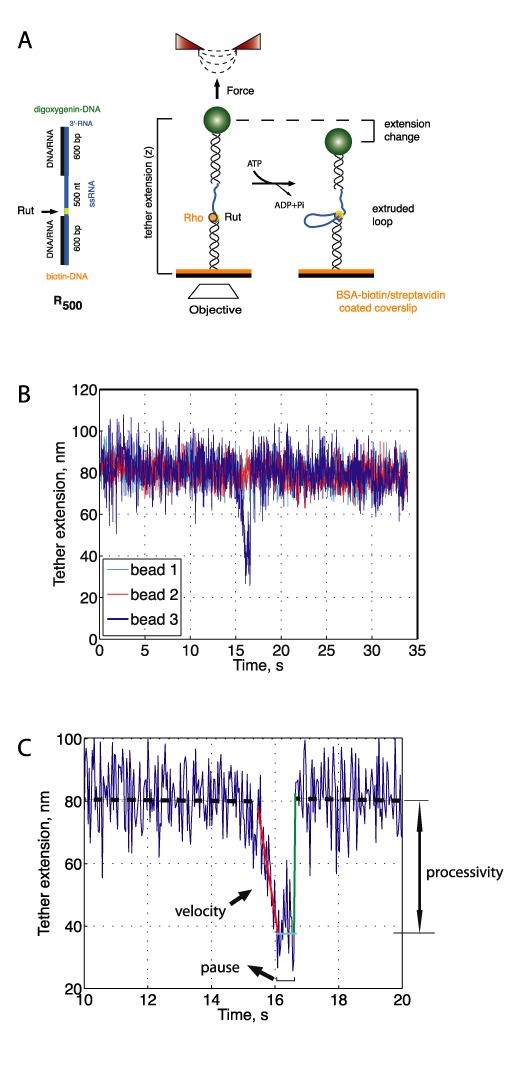
Observing real-time translocation by Rho at the single-molecule level. (A) A magnetic trap (right) consists of a magnetic bead (green sphere) tethered to a glass surface by one tether molecule (black helix and blue line). Magnets above the sample (red triangles) can be translated to exert tension on the DNA molecule. RNA looping by Rho (orange sphere) leads to the shortening of tether extension, monitored by the change in height of the magnetic particle detected through an inverted objective (white rhombus). Handles contain a biotin or a digoxygenin molecule for specific attachment to the BSA–biotin-coated coverslip surface (orange) or an anti-digoxygenin-coated bead. (B) Representative traces of the change in RNA extension due to single-molecule Rho activity on a tether molecule containing a Rut site. Activity of Rho on a single bead (bead 4, blue) in a field of view with several beads (beads 1–3, cyan, red and green) exhibiting no activity. Raw data are shown (34 Hz). Tether extensions represent relative, not absolute measurements of the tether length. Tethers extensions were vertically shifted for clarity. Events were observed at forces > 5 pN. (C) Single-molecule translocation event by Rho in the presence of ATP (raw data at 34 Hz). Forward and backward velocities for each event were obtained by fitting the linear regions (red and green lines represent linear fits) in the extension versus time curve. Forward (backward) velocities correspond to shortenings (recovery) of the RNA extension. Processivity was measured as the height difference between the baseline before the event (black dashed line) and the minimum extension in a event (cyan solid line). Pause length was measured by determining the time spent in a paused state after RNA shortening and before tether extension was fully recovered (cyan horizontal line). In this example, the forward translocation velocity was 90 ± 10 nt/s, the backward rate was 2100 ± 10 nt/s and the pause duration of 0.6 s. In the majority of events (>85%), the RNA extension recovered instantaneously, as shown in this panel.
