Figure 4.
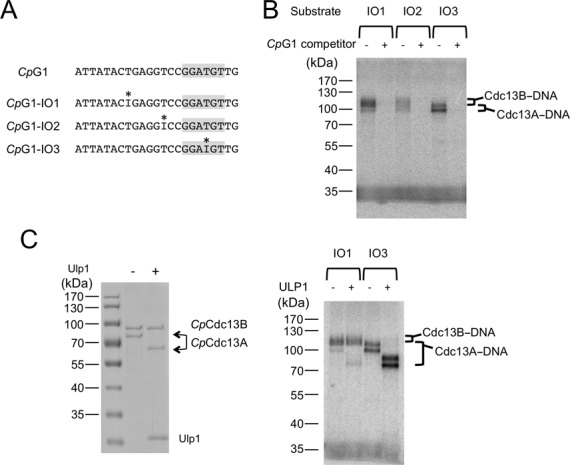
Combinatorial recognition of telomere G-strand by the CpCdc13AB dimer. (A) The oligonucleotides used for the site-specific crosslinking analysis are illustrated. The positions of the 5-Iodo-2’-deoxyuridine analog are indicated by asterisks. (B) The CpCdc13AB dimer was incubated with the indicated oligonucleotides (pre-labeled with P32) and subjected to UV irradiation. The covalent protein–DNA conjugates were separated from free DNA by SDS-PAGE and detected by PhosphorImager analysis. The specificity of the crosslinking reaction was tested by adding 100-fold excess of unlabeled CpG1 competitor to the reactions. (C) Left: The CpCdc13AB dimer was subjected to Ulp1 treatment to eliminate the SUMO tag from the Cdc13A fusion protein. Right: Untreated or Ulp1-treated CpCdc13AB dimer was subjected to crosslinking assays using the indicated substrates.
