Figure 3.
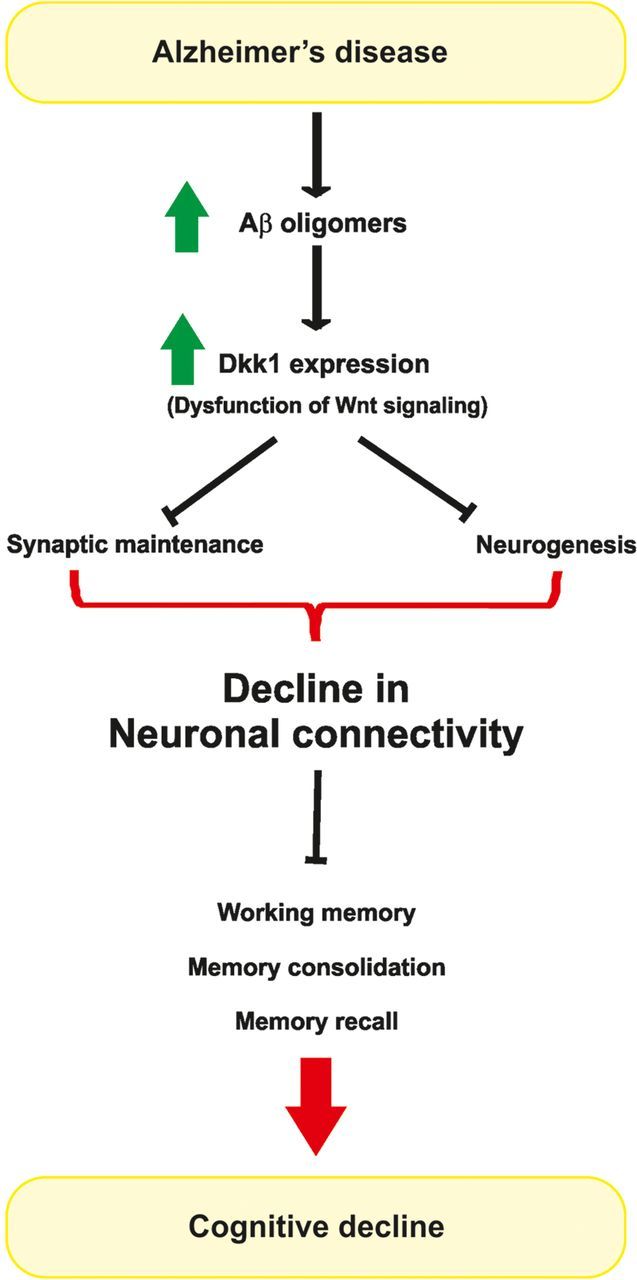
Potential stages in the synaptic pathogenesis in AD. During the disease, accumulation of Aβ oligomers induces the expression of the Wnt antagonist Dkk1. Dkk1 induces synaptic disassembly and inhibits neurogenesis, therefore resulting in a decrease in global synaptic connectivity in the brain. Decline in synaptic connectivity would contribute to impairment in memory, suggesting that Aβ/Dkk1-mediated loss of synapses underlies the cognitive decline observed at early stages of AD.
