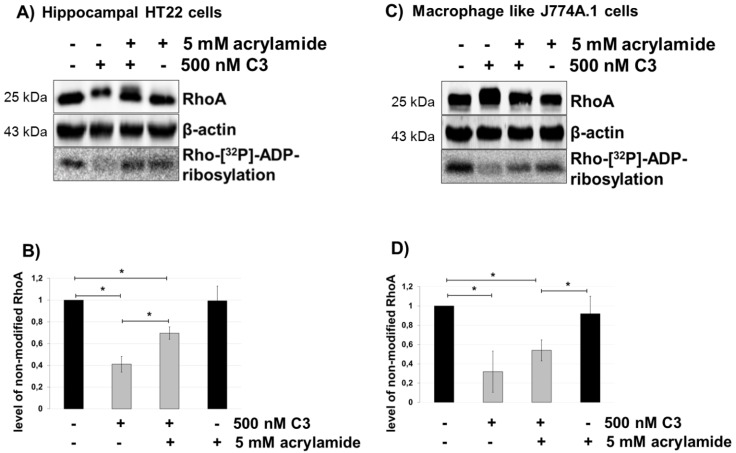
Figure 5.
Uptake of C3 into HT22 and J774A.1 cells after disruption of the vimentin network by acrylamide treatment. Cultivated cells ((A) = HT22 cells, (C) = J774A.1 cells) were pre-treated with acrylamide (5 mM) for 30 min followed by incubation with C3 (500 nM) for the indicated time. Cells were lysed and submitted to western blot analysis probing RhoA and β-actin and the ADP-ribosylation assay. After C3 exoenzyme treatment with or without acrylamide, the cells were lysed, and lysate proteins (4 µg) were subjected to an in vitro [32P]-ADP-ribosylation assay with C3. [32P]-ADP-ribosylated RhoA is quantified densitometrically and normalized to the control level of non-modified RhoA ((B) = HT22 cells, (D) = J774A.1 cells). Statistical differences between C3-treated and control cells were determined using a two-sided Student’s t test (* p ≤ 0.05).