Figure 4. Reactions of benzylic alcohols and alcohol derivatives.
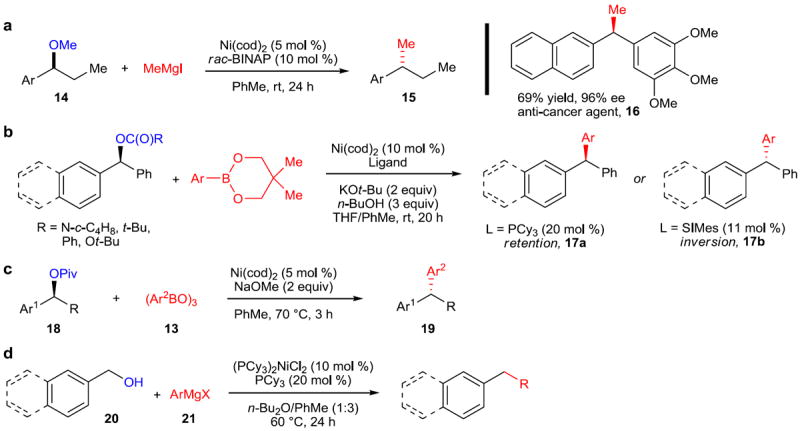
a, Stereospecific methylation of benzylic ethers. A nickel catalyst comprising Ni(cod)2 and rac-BINAP was found to catalyze the methylation of benzylic methyl ethers (14) to form alkyl-substituted arenes (15). A modification for the synthesis of diarylethanes was also devised, allowing the synthesis of the anti-cancer agent 16 in 69% yield and 96% ee. b, A Suzuki–Miyaura-type arylation of benzylic esters, carbonates, and carbamates. The synthesis of triarylmethanes (17) can be achieved by catalytic Ni(cod)2 and PCy3 or SIMes—the stereoselectivity (retention or inversion) is determined by the identity of the ligand. c, A phosphine- and carbene-free nickel catalyst was also developed, yielding inversion of the stereochemistry of benzylic pivalates (18) to provide access to diarylalkanes (22). d, Cross-coupling of free benzylic alcohols. An excess of organomagnesium reagent (21) can be added to form a magnesium alkoxide, which is then a competent coupling partner for the Kumada-type coupling with organomagnesium reagents. rac, racemic; BINAP, 2,2’-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1’-binaphthyl; SIMes, (1,3-Bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)-4,5-dihydroimidazol-2-ylidene); Bu, butyl; Piv, pivaloyl.
