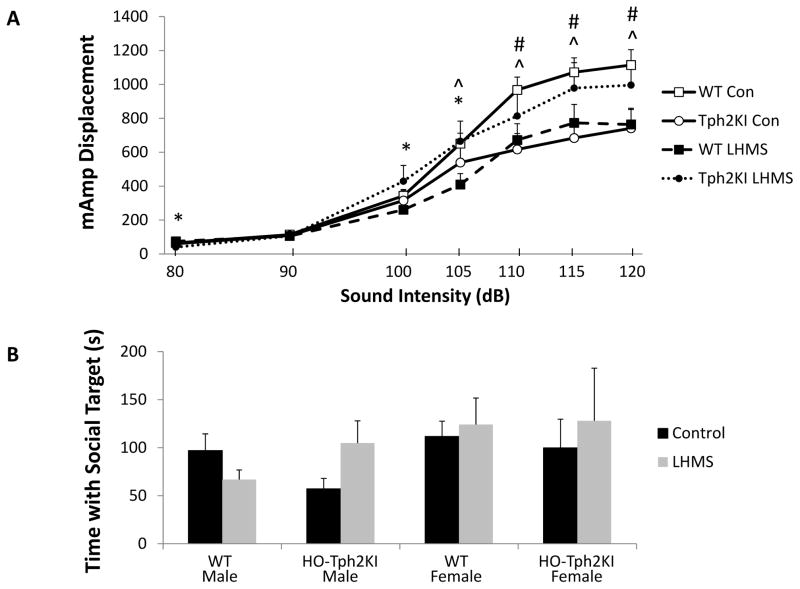
Figure 4.
The effects of LH/MS on acoustic hyper-arousal and social behavior. (A) Startle responses of control and LH/MS-exposed WT and HO-Tph2KI mice across startle intensities. (B) Social affiliation time in male and female WT and HO-Tph2KI mice with an 8 week old, sex-matched animal. N = 15–34 per group for A and N = 15–29 per group for B. Significant genotype by stress interactions were observed by repeated measures two-way ANOVA (for panel A) and by two-way ANOVA (for panel B) (p < 0.05). A significant three-way genotype by stress by startle intensity interaction was also observed in A by repeated measures three-way ANOVA (p < 0.05). * denotes p < 0.05 for WT-LH/MS vs. HO-Tph2KI-LH/MS comparison, ^ denotes p < 0.05 for WT-Control vs. WT-LH/MS comparison, and # denotes p < 0.05 for WT-Control vs. HO-Tph2KI-Control comparison by Bonferroni’s.